| Deficits in Somatosensory Processes
(Anterior Parietal Lesions) |
|
- Heightened somatosensory
thresholds
- "Afferent paresis" (Luria):
clumsiness in fingers due to loss of feedback on
position
|
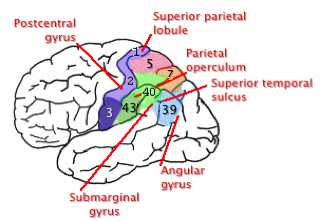
|
- Somatoperceptual disorders
- Astereognosis ("stereo" = "solid" in Greek):
inability to recognize objects by touch (YouTube stereognosis exam
1.15)
- Simultaneous
extinction:
failure to attend to stimuli presented at the
same time
- asomatognosia: loss of a sense of one's own
body including
- anosognosia: denial or lack of
knowledge of illness or impairment (YouTube
4.08 mostly SCZ)
- anosodiaphoria:
indifference toward illness
- finger agnosia: inability to point to or
identify fingers upon stimulation
|
| Posterial Parietal Damage |
Balint's Syndrome (YouTube
1.29)
|
- Inability to fixate on
distinct visual stimuli despite ability to move
eyes
- Simultagnosia:
attention limited to one object at a time
- Optic Ataxia: difficulty
reaching for objects under visual guidance
|
Damage
to BA 5-7 |
Right
Parietal Lesions: Contralateral Neglect et al. (YouTube
3.18)
|
- Neglect for contralateral
(left) side of body
- Neglect for visual stimuli in
left visual field
|
Damage
to BA 39 in R Hemisphere |
- Impairment in object
recognition in unfamiliar views or positions
|
|
Left
Parietal Lesions: Gerstmann Syndrome et al. (YouTube
4.35)
|
- Gerstmann Syndrome
- Finger agnosia
- Right-left confusion
- agraphia (inability to write)
- acalculia (inability to do arithmetic)
- Other disturbances may
include
- Dyslexia
- Dysphasia (errors in
grammar)
- Apraxia [loss of a skilled movement; Dressing Apraxia
YouTube (1.10)]
- Ideomotor Apraxia
= inability to copy movements or gestures
of others
- Constructional
Apraxia = visuomotor disorder in
which subject can't move objects, copy
figures, etc.
- Woman with varying
forms of apraxia [YouTube,
first 5.34)
- Not to be confused
with Childhood Apraxia of Speech
(CAS) in which, despite normal muscles
associated with talking, a child's brain
has major difficulty in sequencing their
movement to create accurate speech. Causes
of CAS are not always clear.
|
? damage
to Angular Gyrus? |
| Drawing |
- Multiple forms of error
ranging from entire drawing to individual details
|
| Disorders
of Spatial Cognition |
- Ability to manipulate spatial
objects mentally may be impaired, e.g., map
reading
|
|