This page was last modified on November 15, 2024
PSY 355 Psychology & Media in the
Digital Age
This page was last modified on November 15, 2024 |
Consumer Behavior
Suppose you were living in the middle of the 20th century (1940-1970).
How would you buy the things you need -- both for daily life and for longer term needs?
Herald Square NY 1940s
Sears, Roebuck Catalog 1950
A&P Supermarket 1960
Some Historical Background to Consumer Culture in the Digital Age
The Rise of Credit Cards
Broadly accepted, bank-based credit cards are central to the ability of people to buy and sell products online & internationally. But, they only began to be used about sixty years ago and, at first, were restricted to individuals with relatively high incomes. In the first half of the 20th century, individual stores (e.g., Macy’s) offered their regular customers credit cards that could only be used in that store.
o 1950: Diners Club card was the first widely-accepted credit card (used mostly in restaurants)
o 1958: American Express card
o 1958: BankAmeriCard (now VISA)
o 1960s: Introduction of magnetic stripe on back of card (standard by 1969)
o 1986: Discover Card (by Sears, now itself a bankrupt corporation)
o 1991: First “loyalty” program by American Express offering “miles”
Although the Equal Pay Act was passed in 1963 requiring men and women to be paid equally when doing the same work, it wasn’t until the Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) was passed in 1974 that women were able to get their own credit cards in their own name. Previously, married women had to get a credit card in their husband's name and unmarried women often could not get one.
Online Security
The World Wide Web (WWW) was designed by Tim Burners-Lee for the European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN in 1989. It is based on the notion of hyperlinks allowing users to go from page to page across the Internet. CERN released the design protocol royalty free to the world in 1993 and, later that year, the first web browser (NCSA/Mosaic) became available for use on personal computers.
The ability to buy and sell products using credit cards over the WWW required that the transactions be secure and free from fraudulent use. The first standard to ensure online security in business transactions was developed in 1994 by Cybersource Corporation, headed by my former student William McKiernan and his colleagues. Their security protocol was directed at medium and large size businesses. Another company, Authorize.net, offered a similar security system for small business payments. Authorize.net was bought by Cybersource in 2007 and, in 2010, Cybersource was bought by VISA.
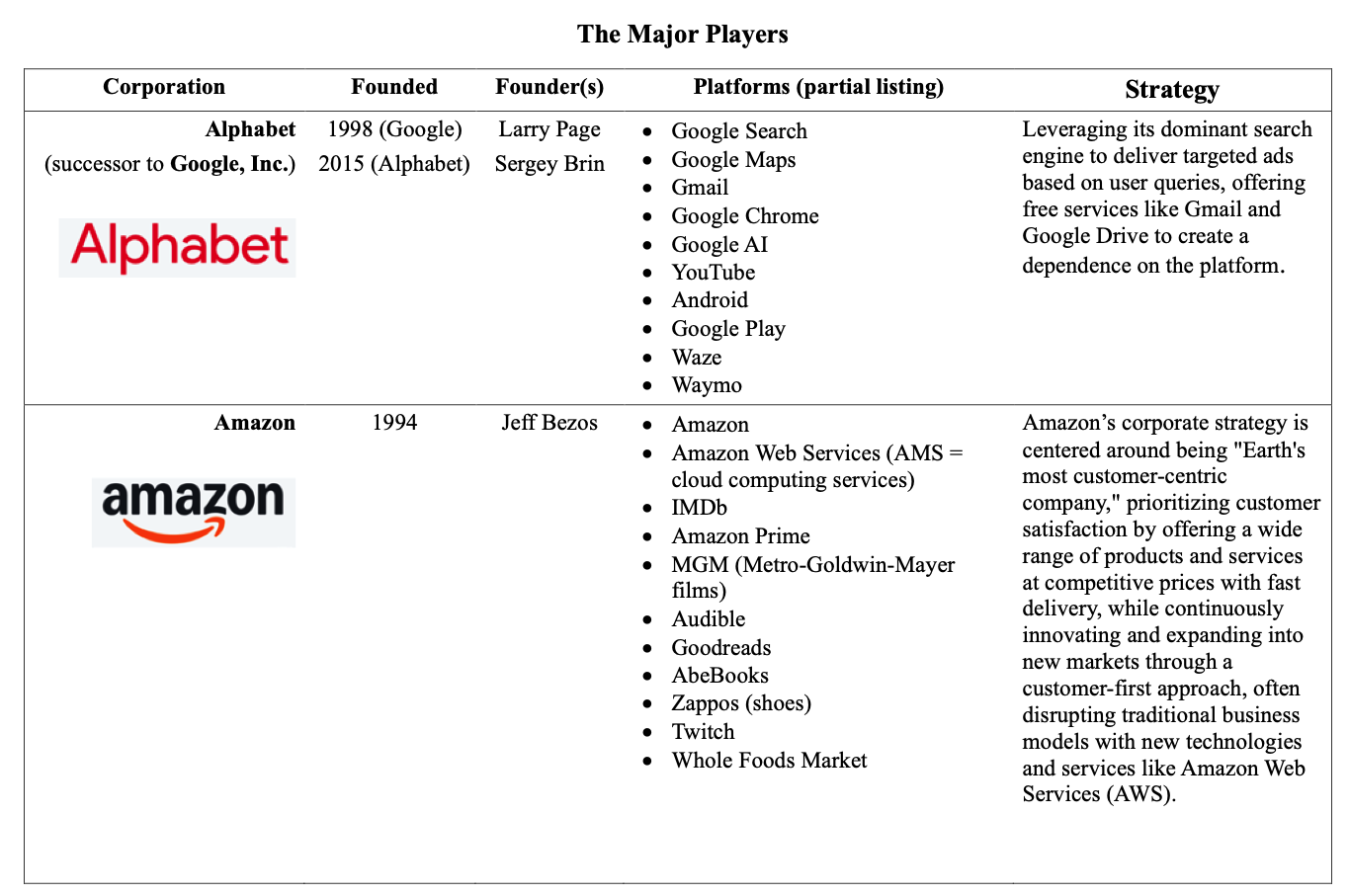
How does
Alphabet Make Its Money
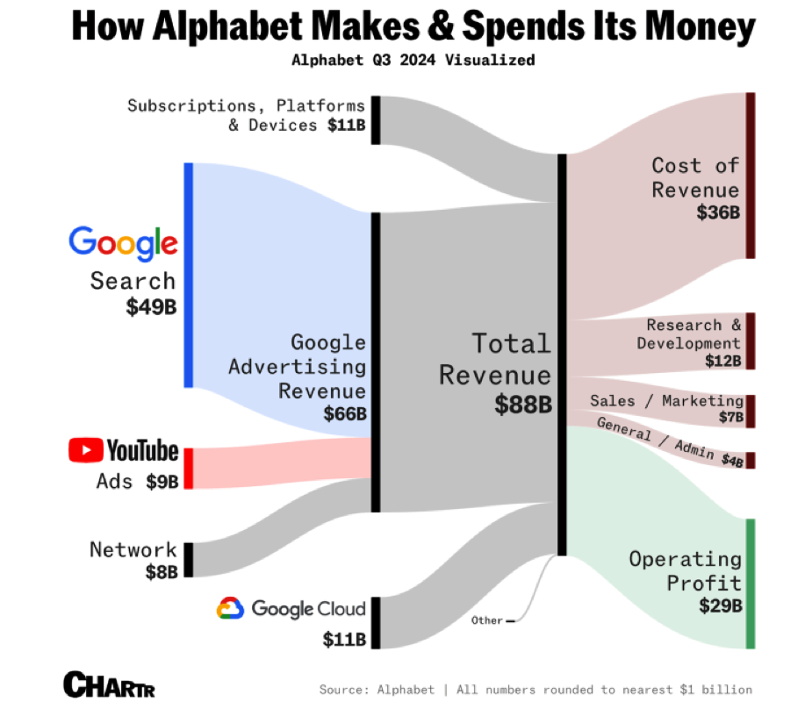 The sources of
income for Alphabet come from five general sources
The sources of
income for Alphabet come from five general sources
• Google Search, adverts on
• YouTube, adverts on
• Google Network Adverts
• Google Cloud (storage)
• Subscriptions to various platforms &
devices
Total Revenue = $88 billion
Total Operating Profit = $29 billion
Profit margin = 33%
Note: A (2024) NYU report on U.S. margins revealed the
average net profit margin is 7.71% across different
industries…As a rule of thumb, 5% is a low margin, 10% is a
healthy margin, and 20% is a high margin.
(https://www.brex.com/journal/what-is-a-good-profit-margin)
Two Google Advertisement Approaches
1. Google AdSense is a free
service that allows website owners to earn money by
displaying ads on their content. AdSense automatically
selects and serves ads on your site based on your content
and audience. You get paid based on how many people view or
engage with the ads. The type of ad determines whether
you're paid per ad impression or per user click.
Who can use it? Independent creators and larger companies
can use AdSense to monetize their websites, blogs, or
forums.
2. Google Ads is an online
advertising platform that allows businesses to promote their
products and services to a target audience. Google Ads uses
a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers bid to
display their ads. Google determines the ad placement based
on the bid amount and other factors. Advertisers can manage
their accounts online, creating and changing campaigns at
any time.
Google Ads can place ads in many different locations,
including:
•
Search results: Ads can appear above or below search results
on Google Search, Google Play, and Google Maps
•
Videos: Ads can appear before, during, or after videos on
YouTube, and on other Google video ad partners
•
Mobile apps: Ads can appear in mobile apps
•
Non-search websites: Ads can appear on partner websites
How has digital media changed the ways businesses approach customers?1. Instant Communications
• Businesses and other organizations seek to be connectable, that is, customers can experience a connection easily and without delay, e.g., research by health provider Kaiser Permanente found that a delay of more than 30 seconds to reach their website’s material dissuaded patients from continuing to connect
2. Content Overload
• The amount of content posted to digital platforms is enormous, e.g., in 2017 3.3 million people posted to Faeebook and 29 million messages were distributed via WhatsApp every minute
• To catch the attention of customers requires attention to simplicity, style, and an emphasis on quality
3. Leveraging Massive Data
• Businesses must be careful to understand what and who they are attempting to influence based upon both their own goals and the nature of their customers
4. Ensuring Transparency
• Customers seek to know about the products they are possibly buying and look for information about what is being sold, e.g., what exactly is in a certain food product
5. Creating a Sense of Personal Intimacy with Customers/Personalization
• By knowing its potential customers, businesses can present them with appeals that reflect their customers’ interests, e.g., tailoring advertising campaigns to the expectations of Gen Y rather than Baby Boomers.
6. Turning to “Influencers” to Promote Products
• Rather than relying chiefly upon known celebrities, businesses are increasingly partnering with more ordinary online presenters who serve to advance various products.
7. Encouraging Innovation
• All major business brands must keep ahead of the changes in media and technology and employ “innovation” labs to test new ideas.