This page was last modified on October 30, 2024
PSY 355 Psychology & Media in the
Digital Age
This page was last modified on October 30, 2024 |
Class 19: The Wonderful World of The Walt Disney Company • Part 1

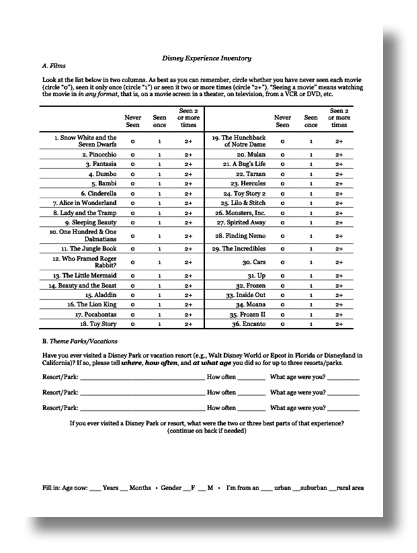 Complete the American Film
Institute Top 10 of Top 10
Complete the American Film
Institute Top 10 of Top 10• Count up the number of films you have seen at least once\
• Count up the number of films you have seen 2 or more times
• Have you ever visited a Disney theme park or vacation resort?
• What did you like about those experiences?
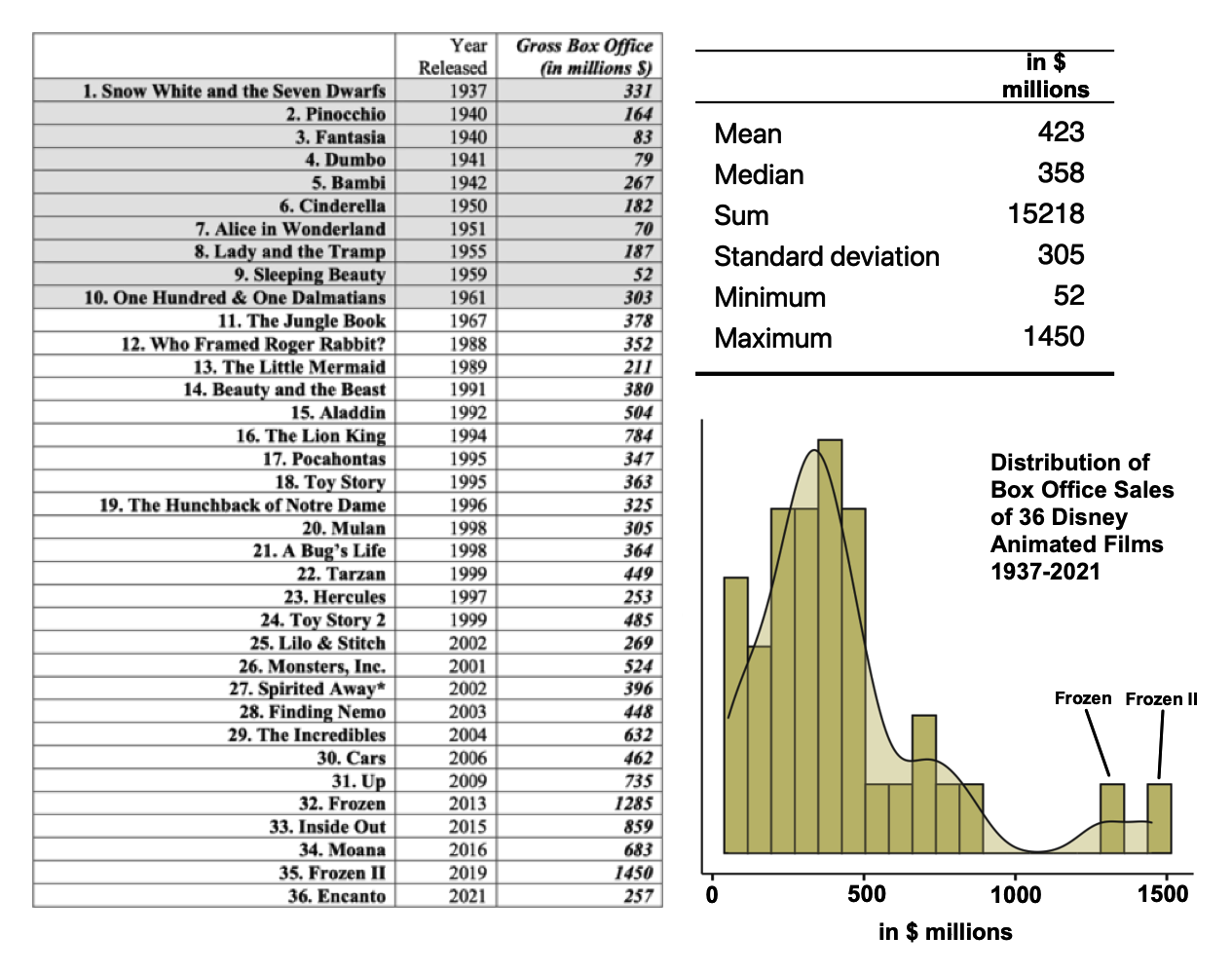
Intellectual property = "the legally recognized exclusive rights to creations of the mind. Under intellectual property law, owners are granted certain exclusive rights to a variety of intangible assets, such as musical, literary, and artistic works; discoveries and inventions; and words, phrases, symbols, and designs." {W}
- vs. Real property: non-movable assets, i.e., buildings & grounds
- vs. Personal property: tangible/movable assets (e.g., jewelry, clothing) and intangible assets (e.g., bank accounts, stocks)
Legal rights associated with intellectual property are grounded in US Constitution, Art. 1, Sec. 8, Clause 8.
Trademarks and service marks: A trademark (for goods, "TM") or a service mark (for services, "SM") is any word, phrase, symbol, design, or combination of these things that identifies a company’s goods or services. Such marks are valid for as long as the trademark is used or the US Patent & Trademark Office rules that the term has become generic, that is, it has become part of everyday language. For example, in the US, all of the following terms used to trademarked by corporations but are now used generically: cellophane, aspirin, escalator, laundromat, linoleum, thermos, trampoline.
- Trademarks can include Logos, Phrases, Sounds, Scents, Shapes & Colors, the overall appearance & image of a product, and fictional characters
- Patents. A patent for an invention is the grant of a property right to the inventor, issued by the United States Patent and Trademark Office. This property right allows its owner to exclude others from making, using, offering for sale, selling or importing the invention. Generally, the term of a new patent is 20 years from the date on which the application for the patent was filed in the United States. There are three types of patents
- 1) Utility patents may be granted to anyone who invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof;
- 2) Design patents may be granted to anyone who invents a new, original, and ornamental design for an article of manufacture; and
- 3) Plant patents may be granted to anyone who invents or discovers and asexually reproduces any distinct and new variety of plant.
- Examples of important patents in the last century:
- 1. Edison’s Light Bulb Patent [1880] (one of 1,100 patents by Edison & his lab)
- 2. Wright Brothers’ Airplane Patent [1903]
- 3. Fleming’s Penicillin [discovered 1928] • technique for mass production patented 1945
- 4. Steve Jobs’ iPhone Design Patent [2012)]
- 5. Marconi’s Wireless Telegraphy Patent [1901, plus another ~800 patents by him/his company]
- 6. Notable Pharmaceutical Patents
- Aspirin by Bayer [1900-1917]
- Viagra by Pfizer (Sildenafil, 1996)
- Prozac (fluoxetine) by Eli Lilly & Co. [1977]
- Lipitor by Pfizer [1997-2011; created $100 billion in sales]
- Insulin [1921]. Sold by discoverers to U Toronto for $1 to make it available worldwide.
- 7. Google’s PageRank Algorithm Patent [1998-2018]
- Copyright: Copyright is a type of intellectual property that protects original works of authorship as soon as an author fixes the work in a tangible form of expression. In copyright law, there are a lot of different types of works, including paintings, photographs, illustrations, musical compositions, sound recordings, computer programs, books, poems, blog posts, movies, architectural works, plays, and so much more!" (U.S. Copyright Office). When this intellectual property is no longer under copyright, it falls into the "public domain" and can be used by anyone.
"The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds the exclusive rights, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission" [Wikipedia, 20230411]
CGP Grey: Copyright - Forever Less One Day (YouTube; 5m12s)
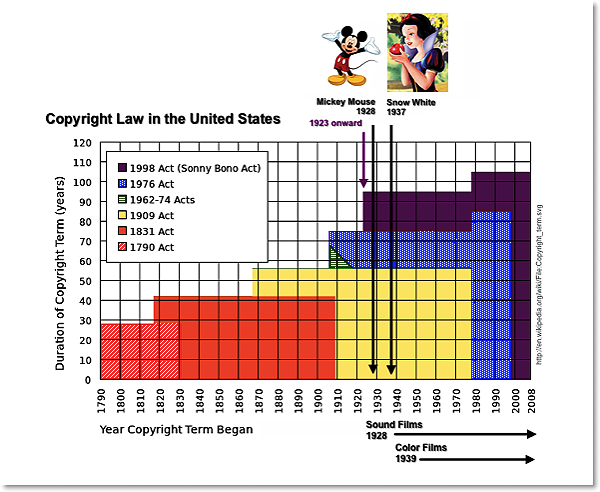 Legal Length of Copyright
Legal Length of Copyright
Historical
- Hollywood: Rise of the great studios (Warner Bros., MGM, etc.) including film production, distribution, and theater ownership (vertical integration)
- The Hearst Corporation in the 1920s & 1930s: magazines & newspapers + Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer (MGM) film company
- 1st commercial radio station: Pittsburgh, PA: KDKA began broadcasting in November, 1920
- NBC (National Broadcasting Company, originally RCA [Radio Corporation of America founded 1926]
- CBS [Columbia Broadcasting System founded in 1927]
- Mutual Broadcasting System founded in 1934 (did not become a television network)
- American Broadcasting Company [ABC founded in 1943]
In the 1950s before the advent of cable television (appearing mostly in the 1970s and 1980s), most larger urban areas had three major television stations that were either owned by or network affiliates of NBC, CBS, and ABC.
Today, those three powerful television networks have been bought out and transformed into major divisions of three of the five largest media companies in the world: Comcast (NBC), Walt Disney Company (ABC), and Paramount Global (see below)
1. Appearance of the corporate than than individual author
2. Legally protected intellectual property owned by corporate authors becomes the foundation of an almost endless series of republication opportunities as new technologies provide new outlets
3. The value of media corporations resides in protecting the ownership of their creations. If they cannot be protected against use by others, the corporation value decreases.
Modern
Corporate Media Conglomerates
Control of the content of more than half of modern mass
media resides in five companies



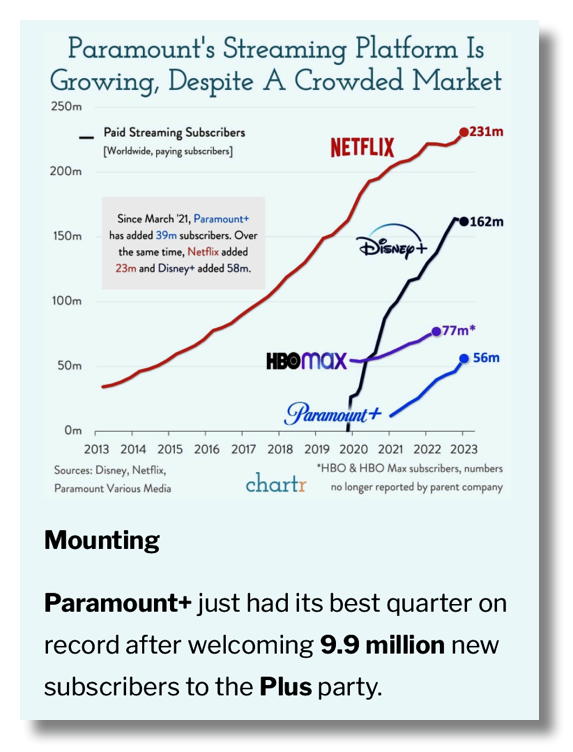
What does Disney own in 2024? (partial listing)

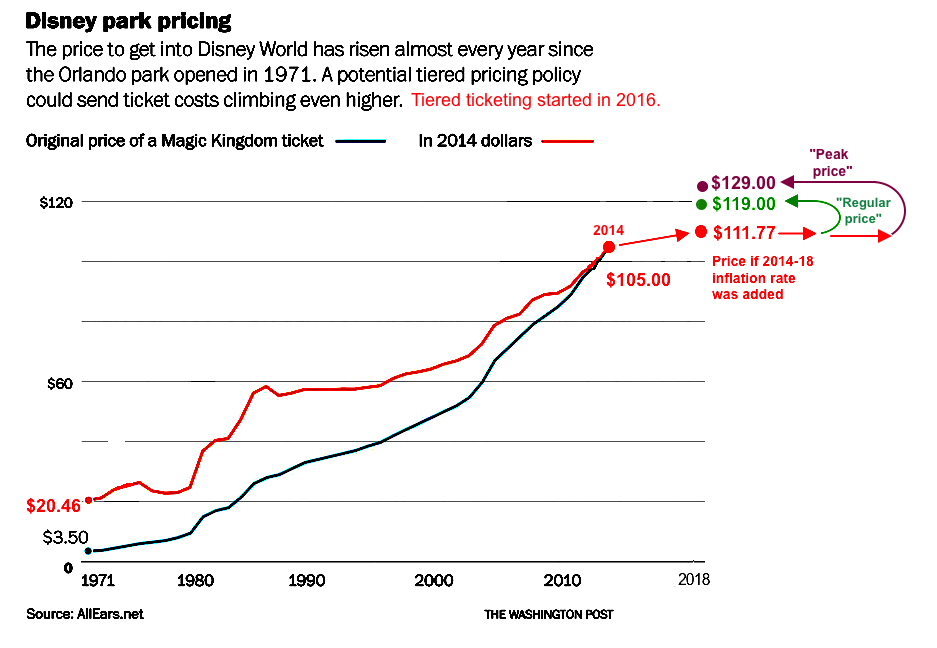
In 2016 Disney began seasonal or "tiered" pricing:
Year Regular • "Peak"
2016: $107 • $119
2017: $115 • $124
2018: $119 • $129
"Regular" tickets in 2018 were $119, but "Peak" season tickets were $129
- A $3.50 ticket in 1971 is equal to a ticket price of $21.37 in 2018
- The rate of inflation between 1971 and 2018 was 611% (average: 13% annually)
- But, instead of costing $21.37, a regular ticket in 2018 costs $119.
- Hence, the REAL cost of a $119 ticket to Disney World in 2018 (that is, the price over and above the inflation rate) went up 557% in these 47 years or an additional 11.9% annually.
During the pandemic (2021) with a scarcity of customers, Disney World Orlando lowered its base price per person age 10 or older.
What about 2024?
Pricing in 2024 for Disney World includes the following range
How many days?
Price Range
Ticket cost per person + Sales Tax
Total Ticket cost per person 1-Day
$109-159
$109-159 + $7.09-10.34
$116.09-169.34
2-Day
$107-155
$214-310 + $13.91-20.15
$277.91-330.15
3-Day
$105-$149
$315-447 + $20.48-29.06
$354.48-476.06
4-Day
$102-149
$408-596 + $26.52-38.74
$434.52-634.74
5-Day
$97-129
$485-645 + $31.53-41.93
$489.53-686.93
- Water Park and Sports add-on option: Visit one theme park per day, plus enjoy a certain number of visits to a water park or other Walt Disney World fun. A 2-day ticket allows two visits, a 3-day ticket allows 3 visits and a 4-day ticket allows 4 visits. Cost: $35 per ticket per day
- Park Hopper Plus add-on option: Visit more than one theme park on the same day, plus enjoy a certain number of visits to a water park or other Walt Disney World fun. A 2-day ticket allows two visits, a 3-day ticket allows 3 visits and a 4-day ticket allows 4 visits. Guests must make a theme park reservation for the first park they plan to visit. After entering that first park, Guests will be able to visit the next park starting at 2:00 PM until each park’s regularly scheduled closure. Cost: $55 per ticket per day
Note that there are different prices for children and adults as well as additional charges for express entry to rides, etc. Finally, Florida charges a tax of 6.5% on ticket sales as shown above.
The cost of a 5-day BASELINE trip to Disney World Orlando for a family of 4 (2 Adults, one child over 10, and one child 3-9 years old) in 2025 will be $7,093 ($355 per person per night). For a family of 3 (two adults & one younger child). the cost is $5,646. For a family of 5 (two adults, one older & two younger children, which requires a different hotel, the cost is $8,856.
The BASELINE price includes flights, transportation to/from Disney World, 5-night stay at Pop Century, five day tickets without park hopper, Lightning Lane Multi Pass at two parks (Magic Kingdom & Hollywood Studios), quick service meals, snacks, and two table service meals.
The expensive trip version (includes park hopper tickets, more Lightning Lane Multi Passes, and some Single Pass Lighting Lanes), upgraded dining, et al., comes to
- $8,909 for a family of three
- $10,770 for a family of four
- $12,433 for a family of five
What about the income of Americans to pay these price increases?
\