PSY 355 Psychology & Media in the
Digital Age
This page was last modified on September 26, 2024
PSY 355 Psychology & Media in the
Digital Age
This page was last modified on September 26, 2024 |
Today's and next Monday's classes will look at the Impact of Techno-Digital Media on Human Cognition & Mental Activity
Class 13: The Neuropsychology of Media • I • The Impact of Light (Outline)
A. Circadian Rhythm
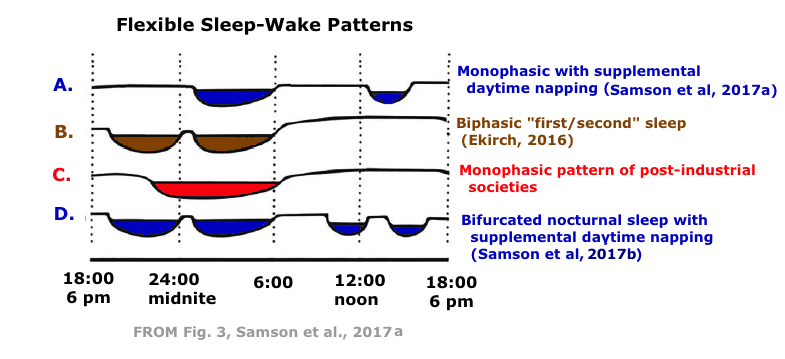
B. Sleep in Post-Industrial Societies
- Post-Industrial Societies: Services > Goods
- Sleep is monophasic (6-8 hours)
- Alternating NREM (Non-REM) and REM (rapid eye movement) periods of sleep
- NREM longer in 1st half; REM longer in 2nd half
- Sleep needed for immune function, efficient metabolism, cell maintenance and repair, memory consolidation, creativity & innovation, and emotional regulation
- Chronic sleep deprivation and/or disruption in circadian rhythms => obesity, hypertension, immune system dysfunction
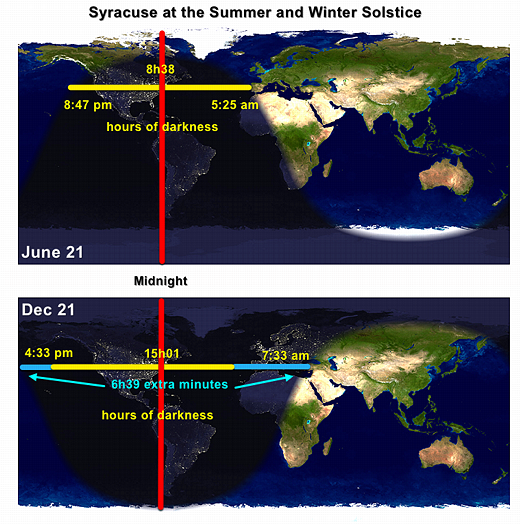
C. Before the 19th Century & the Industrial Revolution in Europe: A World of Extended Darkness
1. Nighttime before the Industrial Revolution in Europe

- The night was populated by "fear, fire, and Satan" (Refford, 2009, p. 780)
- If daylight was the time of goodness and God, the night was the time of evil and the Devil
- In a world of streets that had little or no light, the chance of crime increased.
Higher levels of drunkenness, violence, and murder.
- What was available to the ordinary family who had shut themselves into their homes?
2. "Segmented" or "Biphasic or Divided Sleep" in Pre-Industrial Societies
- Separated or Biphasic sleep (biphasic = sleep in 2 parts)
- "First Sleep"
- Quiet Wakefulness
- "Second Sleep"
3. Changes brought by the Industrial Revolution & Techno-Digital Culture
- Indoor Lighting (Pauley, 2004)
- Shiftwork {W} & health problems
- Transatlantic Travel {W} & Jetlag
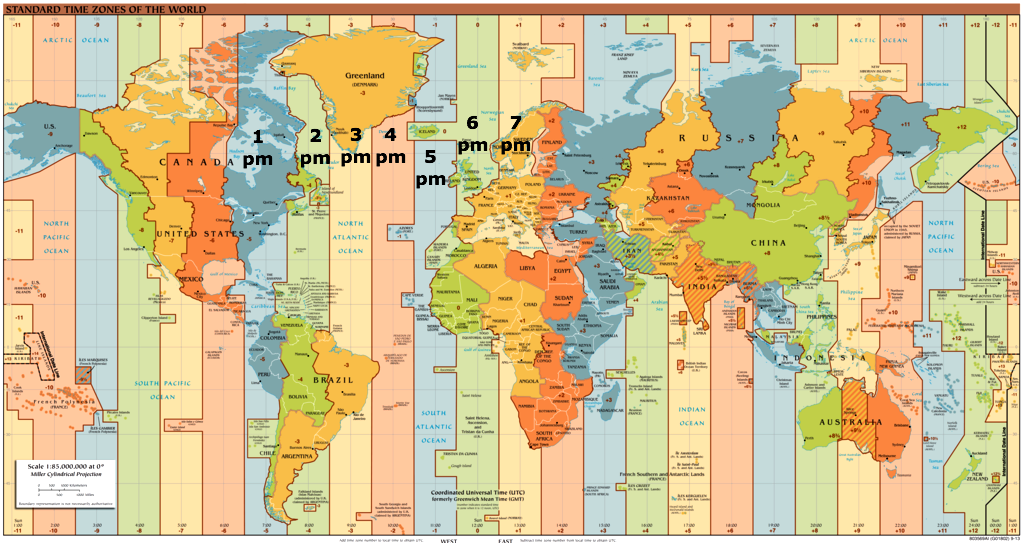
- Social Jetlag
- Entertainment & Communication Media & Light
This page was first posted on 2/24/14