|
|
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 41: Mood Disorders [Outline] |
|
|
|
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 41: Mood Disorders [Outline] |
|
A. Major Depressive Disorder (DSM-5)
Psychiatric Interviews for Teaching: Depression (2012) University of Nottingham, UK YouTube (14'44") |
 |
 Individuals
with Major Depressive Disorder tend to
Individuals
with Major Depressive Disorder tend to
Notice the wide discrepancy among the states for hospitalization rates for depression
Gender & Age: Incidence & Prevalence
- Depression is about twice as common among adult women than adult men across the life span in cross-cultural studies in the US and elsewhere
- 12-month prevalence in the United States among all adults in 2021 was 8.3% (ca. 21 million American adults)
- In US, one-year prevalence was 6.2% in men & 10.3% in women in 2021
- However, young adults (18-29 years old) were more than 4 times as likely to experience MDD as adults over age 50: 18.6% vs. 4.5%
- In US, lifetime incidence is ca. 12% in men & 20% in women
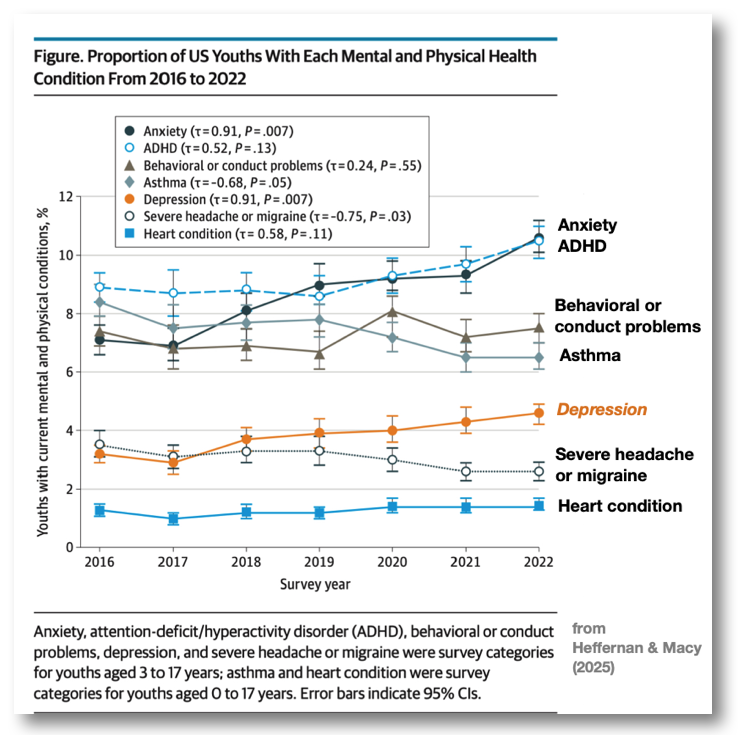
- Childhood depression appears to be equally common in boys and girls before 13 years of age.
- The estimated prevalence among pre-schoolers and pre-pubescent children is around 2%.
- However, among adolescents between 13 and 18, the rates become much higher: 7.5% 12-month prevalence and 11% lifetime incidence with girls being twice as likely to be diagnosed as boys
- These data from before the Covid-19 pandemic have been supplanted as the rates of depression, anxiety, and other forms of mental disorders among children and adolescents have risen in the past 5 years.
- Latest data shows increase of depression in youth 3 to 17 years old from 3.2% (95% CI 2.9%-3.5%) in 2016 to 4.6% (95% CI, 4.2%-4.9%) in 2022 (Heffernan & Macy, 2025)
- Similarly, the rate of anxiety has also increased post-pandemic: from 7.1% (95% CI, 6.6%-7.6%) in 2016 to 10.6% (95% CI, 10.1%-11.2%) in 2022
1. Genetics
- Evidence of genetic or other biological predispositions to depression shows a moderate degree of heritability.
- The heritability of depression is lower than the heritability of schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
- Unsurprisingly no single gene for depression has been found
- Researchers had hoped to find a gene by environment (GxE) effect where certain genetic vulnerabilities interact with stressful environments to produce depression. Our text cites the Serotonin Transporter Gene (5-HTTT) Stress Sensitivity Hypothesis of Caspi et al (2003).
- Recent research by Culverhouse et al (2017) has disproven the Caspi et al (2003) study. They could not demonstrate a GxE effect. But, they did find life stressors and female sex WERE each strong and independent risk factors for depression.
- A recent major GWAS of depression among 689,000 participants with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and 4.4 million controls from 29 countries across the globe found 697 genetic markers for the development of MDD at 635 positions on chromosomes of which 293 were not previously known. However, the overall ability to predict MDD based on these genetic variants is quite modest: about 6%.
2. Course of Depression
- Depression is usually episodic, not constant: episode generally lasts about 6-7 months.
3. Postpartum Depression (not in book)
- Most women experience the blues for a day or two after giving birth.
- About 20% experience moderate postpartum depression (depression after giving birth) and 1/10 of 1% experience very severe postpartum depression.
4. Brain Functioning and Structure
- Most people suffering from depression have decreased activity in the left prefrontal cortex and increased activity in the right prefrontal cortex.
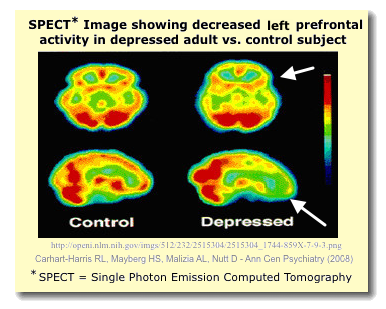

- Left hemisphere brain damage leads to more severe depression than right hemisphere damage.
- Decreased volume of cortical and limbic brain regions. The size of cells in both the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus has been reported as smaller than normal. Stress-related depression show overall decrease in the number of dendritic branches, dendritic spines, and overall synaptic complexity.
5. Antidepressant drugs
a. Tricyclics
b. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The most popular drug in this class is fluoxetine (Prozac®).
c. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
d. Atypical Antidepressants
- bupropion (Wellbutrin®), which inhibits reuptake of dopamine and to some extent norepinephrine
- venlafaxine (Effexor®), which inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine; and
- nefazodone (Serzone®), which specifically blocks serotonin type 2A receptors and blocks reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine.
e. St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L) is an herbal treatment of depression
- WARNING: May increase breakdown of medicines in the liver as well as the effectiveness of contraceptive medications.
- Dosage & purity levels may vary
f. Time: Delayed Effects: Most of antidepressants have delayed effects, i.e., they require 2-3 weeks for beneficial effects to appear.
- A possible reason for the delay may involve a gradual increase in the release of BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor)
- May desensitize the autoreceptors to increase the release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin.
Ketamine {W} as Rapid Treatment for Depression
- Ketamine is a nonselective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist. Glutamate, the excitatory transmitter, binds to NMDARs which are found throughout the nervous system (including the membrane of both neurons and glial cells [astrocytes]). Used as an anesthetic in animal surgery, Ketamine ("Special K") as a recreational drug can damage brain cells.
- Research in last decade showed that intravenous-injected Ketamine could have a rapid effect in relieving symptoms of depression (within hours rather than days/weeks.)

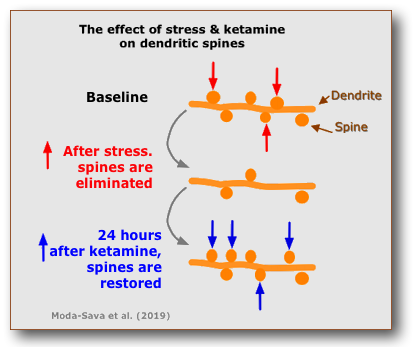
- In March 2019 the FDA approved the use of a new nasal spray medication, Spavato, with its active ingredient, Esketamine (a molecule quite similar to Ketamine), for treatment-resistent depression.
- Moda-Sava et al (2019) studied the effects of chronically-stressed mice and found that (1) stress caused damage to dendritic spines in their brains and (2) ketamine caused the growth of new dendritic spines within 24 hours. This may be one of reasons why Ketamine may help in depression.
- However, one commentator argues "Anyone who tells you that they know how ketamine works for depression is kidding themselves” (Lowe, 2023).
g. Controversy: Serotonin Hypothesis of Depression = depression is caused by too little serotonin in the brain.
Increasingly neuroscientists reject the "Serotonin Hypothesis of Depression" completely or substantially
- Irving Kirsch: The Emperor's New Drugs: Exploding the Antidepressant Myth (2010)
- University of Pennsylvania researchers (Fournier et al. 2010) reexamined the six most rigorous studies of the effectiveness of antidepressants vs. placebos.
- Patients with mild to moderate depression show relatively little benefit from antidepressant medications
- Patients with severe depression respond "substantially" to medications over a placebo
6. Non-Drug Therapies
a. Psychotherapy (particularly, cognitive therapy & interpersonal therapy) and drug therapies produce similar effects on brain activity.
b. Aerobic Exercise
c. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
d. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Severe, Treatment-Resistant Depression
Bipolar disorder (BD, formerly
Manic-Depressive Disorder)
Bipolar Disorder • Manic State Interview Psychiatric Interviews for Teaching: Mania University of Nottingham |
 |
Disorder where the person alternates between episodes of depression and mania (= restless activity, excitement, laughter, self-confidence, rambling speech, and loss of inhibitions). BD patients have wider mood variations or instability even in periods of good mood ("euthymia")
Mania: = persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, and abnormally and persistently increased activity or energy. It is characterized by at least three or more of the following symptoms (DSM-5-TR, 2022):
- Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity
- Decreased need for sleep (e.g., rested after only 3 hours of sleep)
- More talkative than usual or pressured to keep talking
- Flight of ideas or subjective experience that thoughts are racing
- Distractibility (easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant external stimuli)
- Increased in goal-directed activity (socially, at work, sexually) or psychomotor agitation (i.e., purposeless non-goal-directed activity)
- Excessive involvement in activities that have a high potential for painful consequences (e.g., unrestrained buying sprees, sexual indiscretions, foolish business investments)
- The manic/hypomanic episode usually precedes the depressive episode.
 Lithium salts (e.g., Eskalith® =
lithium carbonate)
Lithium salts (e.g., Eskalith® =
lithium carbonate) 
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
![[Winter Solstice: Dec 21]](../graphics/winter.solstice.jpg)
1. SAD is most common in the North Hemisphere in those areas where the nights are longer in winter and shorter in summer.
- In the extreme European and North American north, native peoples tend NOT to have increased SAD during winter months. This may represent an evolutionary adaptation.
- Individuals who are "morning people" ("Larks") tend to show higher rates of SAD in the winter than those who are "night people" ("Owls")
- There IS a version of SAD that occurs among some people each summer. This form of SAD is not well understood. It may be related to warmth/heat rather than levels of light.
2. It is not completely clear what the cause(s) of Seasonal Affective Disorder may be. Suggested mechanisms include
- Disruption in the biological clock (i.e., circadian rhythms) because of the changes in available sunlight in the winter
- Decreased levels of serotonin which may be induced by the decrease in sunlight
- Melatonin levels may be disrupted as well with an increase in melatonin overall leading to feelings of sleepiness.
3. Light Therapy (Phototherapy) & dawn simulation.