|
April 06, 2025 |
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 36: Lateralization of Function [Outline] |
|
|
April 06, 2025 |
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 36: Lateralization of Function [Outline] |
|

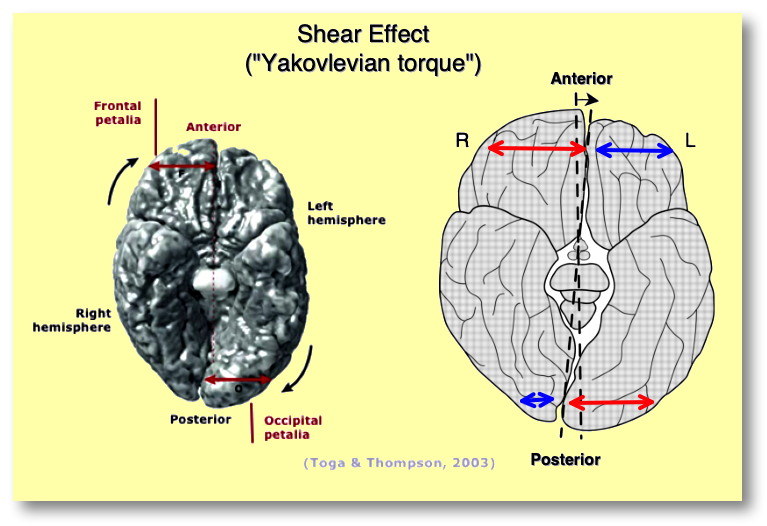
A. The Right and Left Hemispheres
Lateralization: Refers to those behaviors and cognitive abilities that each hemisphere specializes in.
Contralateral = the other side while ipsilateral = the same side
Function
Left Hemisphere
Right Hemisphere
Muscles
Contralateral (right side)
Contralateral (left side)
Skin Receptors
Contralateral (right side)
Contralateral (left side)
Vision (Eyes)
Contralateral (Right visual field of both left and right eyes; see diagram below)
Contralateral (Left visual field of both left and right eyes; see diagram below) Hearing (Ears)
Information from both ears, but stronger from right ear
Information from both ears, but stronger from left ear
Taste
Ipsilateral (left side of tongue)
Ispilateral (right side of tongue)
Smell
Ipsilateral (left nostril)
Ipsilateral (right side of tongue)
Trunk Muscles & Facial Muscles
Jointly controlled
B. Visual and Auditory Connections
Visual Processing.
- Right visual field
left half of each retina
left hemisphere
- Left visual field
right half of each retina
right hemisphere
Auditory Processing. Information from each ear is transmitted to both sides of the brain.
C. Corpus Callosum and the Split Brain Operation
The corpus callosum is a massive set of axons which allow the two hemispheres to exchange information with one another. There are two other major commissures: the anterior commissure and the hippocampal commissure [note: there are also two other even smaller commisures: the posterior and habenular].
1. Severing the corpus callosum prevents the sharing of most information between the brain hemispheres.
2. Epilepsy
YouTube Video. Video of a grand mal (tonic-clonic) seizure (1'18") of a college-age man, Josh. (Note that this is a graphic video.)
Most people with epilepsy (90%) can control their condition with medications that suppress seizure activity. Surgery for epilepsy can take two forms. The earliest form sought to remove any focus of epileptic activity.
3. Commissurotomy (also called corpus callosotomy)
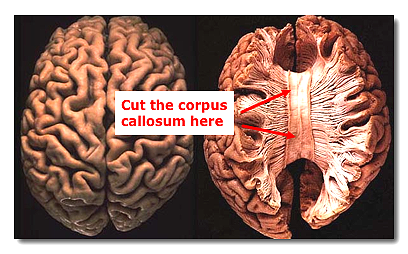
- These individuals are often referred to as split-brain people. Operations began in 1962 to relieve epilepsy that otherwise would not remit.
- Roger W. Sperry (1913-1994) who researched the effect of severing the corpus callosum in cats. Sperry won Nobel Prize in 1981 for his work.
- He and Michael Gazzaniga began to study the effects of split-brain operations on patients and what those operations revealed about the functioning of each hemispshere of the brain.
4. Studying Split-Brain Patients.
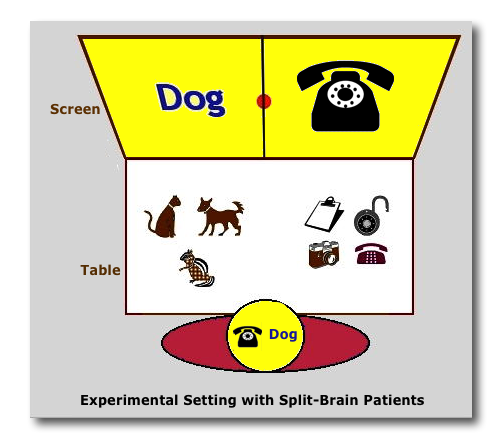
YouTube Video: Split-brain patient 'Joe' being tested with stimuli presented in different visual fields (10'11" total; 1st 4 min. for this class)
- "left hemipshere interpreter" = create stories to account for unconscious or unexpected experiences.
- The right hemisphere is much more tied to what is concrete and "real".
5. The Right Hemisphere vs. the Left Hemisphere: Some Differences
a. The right hemisphere is better than the left at perceiving the emotions in people's gestures (non-verbal or paralinguistic information).
b. People with right hemisphere damage speak with less inflection and expression, plus they often have trouble interpreting the emotions that other people express through their tone of voice (prosody).
c. Research findings suggest that the right hemisphere is more adept than the left at comprehending spatial relationships.
d. The left hemisphere is more focused on details and the right hemisphere is better at perceiving overall patterns.
Role of Left Hemisphere Role of Right Hemisphere Speech Production of speech, comprehension of the literal meaning of speech Emotional inflections, understanding jokes & humor, sarcasm, emotional content of speech Auditory System Sounds related to speech Non-language environmental sounds (e.g., rain)
MusicEmotions Expressions of happiness & anger (= denial of happiness)
Expressions of fear, disgust, sadness; interpreting the emotional expressions of other people Vision Details Overall configuration;
spatial processing (e.g., arranging pieces of a puzzle or drawing a picture)Mode or Style
(How data are processed)Details, parts, pieces Gestalt, overall configuration; global form
D. Development of Lateralization and Handedness
1. Planum temporale: A section of the temporal cortex that is larger in the left hemisphere in approximately 65% of the population.
2. Corpus Callosum. The corpus callosum matures slowly over the first 5 to 10 years of human life. It contains roughly 200 million fibers that cross from one hemisphere to the other.
3. Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum (ACC).
The following two commissures are often larger than normal in people born without a corpus callosum:
a. Anterior commissure: A very tiny bundle of fibers (about 3.5 million, see image below) that connects the two hemispheres around the anterior parts of the cerebral cortex.
Its major role in people with an intact corpus callosum involves olfaction (smell) and other functions which are not as well understood. In ACC, this commissure seems to convey visual information, a role it typically does NOT play.
b. Hippocampal commissure: Connects the left hippocampus to the right hippocampus. Its general role is not well understood but may involve recognition memory.
Handedness
- Roughly, 90% of population is right-handed and 10% either left-handed or ambidextrous.
- General estimate of left hemisphere dominance for speech: roughly 95% of right-handers & 80% of left-handers.
- Many left-handers also show greater than normal spatial processing on the left (not right) side.
- Right-handers have preference for turning left and left-handers a preference for turning right when confronted with forks in the road.
- As we will see, McGilchrist links the left hemisphere with seeking out prey which is usually caught/grasped by the right hand.
Avoiding Overstatements
What is the answer to the first question at the beginning of this lecture?
Are there "right-brained" and "left-brained" people? NO: This is a myth!
As our text points out, such claims are based on two correct and one incorrect assumptions:
- each hemisphere specializes in particular functions [TRUE]
- tasks involving particular functions evoke higher levels of activity in particular hemispheres [TRUE]
- individual persons rely more heavily and most of the time on one of the hemispheres [FALSE]
We do not have scientific evidence to support that last claim: relying upon either the right or the left hemisphere habitually.
- Indeed, the presence of the corpus callosum means that the brain is constantly engaged in interhemispheric communication: one side of the brain is always in conversation with the other side of the brain.
- Most cognitive processes (including creativity, imagination, seeing details, doing mathematics, understanding language, etc.) actually rely upon functions of both hemispheres.
However, we will see more about right versus left brain functioning in the next lesson on the work
of Dr. Iain McGilchrist and this theory of The Master and the Emissary.