![[Brain Image]](../graphics/head_space.gif)
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior
Class 10: Structure of the Vertebrate Nervous System OUTLINE
|
|
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 10: Structure of the Vertebrate Nervous System OUTLINE |
|
Structure of the Vertebrate Nervous System
A. Terminology to Describe the Nervous System

Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System (CNS)
Any nerve that does not belong to the CNS
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Enteric Nervous System (ENS): Usually seen as part of ANS (more below)
Directions in the Nervous System
Rostral from ROSTRUM - A bird's beak [& the prow of a ship]
Dorsal from DORSUM - An animal or person's back
Ventral from VENTER - The belly or abdomen
- A ventriloquist speaks from the belly.
Caudal from CAUDA - The tail of a horse
- The origin of the word, coward, since one sees the tail of the horse when a horse rider flees from battle
Superior is ABOVE while Inferior is BELOW
Proximal is NEAR while Distal is FARIpsilateral occurs on the same side
Contralateral occurs on the other side
- Lamina (laminae, pl.)
- Column
- Tract (Projection)
- Nucleus (nuclei, pl.)
- Ganglion (ganglia, pl.)
- Gyrus (gyri, pl.)
- Sulcus (sulci, pl.)
- Fissure
B. The Spinal Cord
Bell-Magendie law
- sensory information enters by way of the dorsal roots (in the back)
- motor information to the muscles and glands exits by way of the ventral roots (out the front)
- dorsal root ganglion (ganglia, plural)
- "Gray matter" in middle = cell bodies
- "White matter" surrounding = insulated axons
C. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
1. Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic branch of the ANS prepares the body for action: fight or flight.
2. Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic branch of the ANS helps to restore the body, build up energy & supplies needed in the future, and relax.
3. Drugs & the ANS
- Norepinepherine in PNS
- Acetylcholine [Ach] in SNS
- OTC drugs either suppress the PNS and/or stimulate the ANS leading to dry mouth & increased heart beating.
4. GI Tract and Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
- GI Tract
- ENS: lines walls of GI tract organs. Can function independent of CNS
- Food propulsion, nutrient handling, blood flow, immunological defense
- Microbiome (organisms in GI tract) can have effect upon behavior via signals to CNS
The Brain: Divisions
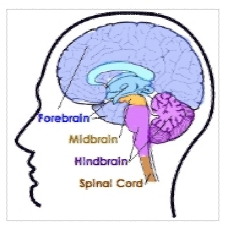
- Hindbrain
- Midbrain
- Forebrain
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
- Basal Ganglia
- Basal Forebrain
- Hippocampus
- Cerebral Cortex (in the next class)
Hindbrain
Chase with his older brother
Medulla (oblongata) Pons (the "bridge")
Cerebellum ("little cerebrum" or "little brain" with ca. 70 billion neurons)
- Ascending reticular formation/ascending reticular activating system
- Raphe system: major serotonin system
- Movement & balance
- Time-related behaviors (rhythm, drum playing)
- Simple learning & conditioning
- NEW: role in cognition, language, & affect (emotion)
- Anterior: motor & movement
- Posterior: cognition, language, affect
- Rapid model building of body interacting with the world around it
Agenesis of the Cerebellum [No or partial cerebellum at birth]
Chase Britton - Boy Without a Cerebellum (and Pons)
YouTube Video
Update (9/17/2013): Chase is now 6 years old, has begun 1st grade (he was in kindergarten 2012-13), plays with his older brother Alex on his iPad, can count to 30, reads short words, and has a service lab/Great Dane dog named "Missa".
Update (8/14/14): Chase attended and met with Lady Antebellum at the Erie County Fair this year.
Updates in Dec. 2019 & May 2020. Chase is now 12-13 years old, uses both a wheelchair and a special walker. His father, David E. Britton, unfortunately died of stomach cancer at age 50 in May, 2020.
2025 No new updates on Chase who would now be 17-18 years old
Chinese Woman, 24, found to lack cerebellum (2014)
In what seems to be only the 9th documented case, a 24-year-old woman in China went to the hospital complaining of a headache and was found to have been born without a cerebellum.Feng Yu et al. (2014)
45-year-old man in India found to lack cerebellum (2018)
Midbrain
Tectum ("roof")
- Superior Colliculus ("upper little hill"): Visual orientation
- Inferior Colliculus ("lower little hill"): Auditory orientation
Tegmentum ("floor covering" or "rug")
- Ascending sensory & descending motor tracts pass through
- Regulation of movement (e.g., eyes)
- Pain modulation
Substantia Nigra ("dark substance")
- DA neurons required for smooth muscle control
- Loss = Parkinson's disease
Forebrain
Outer surface = Cortex (Latin = Bark of tree) [in next class]
Limbic System (linked set of structures beneath the cortex including olfactory bulb, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, & cingulate gyrus)
Thalamus ("antechamber")
Hypothalamus ("beneath the thalamus")
Pituitary Gland
Basal Ganglia
caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus Basal Forebrain
- nucleus basilis
Hippocampus ("sea horse")
Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex - Covered in next class
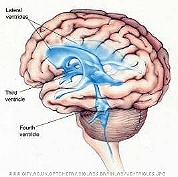
Ventricles and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- cerebrospinal fluid [CSF]: Clear, colorless, watery substance akin to blood plasma
- shock absorber or cushion and support for the weight of the brain
- nutrition (vitamins, hormones)
- waste removal
- CSF is formed by the choroid plexus within the ventricles
- CSF flows throughout the ventricles and around the extracelluar space of the brain
- CSF is reabsorbed into the blood stream via the meninges
This page was first posted February 6, 2005