![[head]](../graphics/head.gif)
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior
Class 09: Substance Abuse and Addiction (Outline)
|
|
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 09: Substance Abuse and Addiction (Outline) |
|
- DMX (1970-2021). Rapper. Drug-induced (cocaine) heart attack.
- Taylor Hawkins (1972-2022). Drummer for Foo Fighters. Apparent heart disease/attack. Multiple drugs found in his system at the time of death included opioids, benzodiazepines, tricyclic antidepressants, and THC (active ingredient in marijuana, see below).
- Jimi Hendrix (1942-1970). Musician. Alcohol & barbiturate overdose. Inhalation of vomit.
- Philip Seymour Hoffman (1967-2014). Actor. Heroin overdose.
- Whitney Houston (1963-2012). Singer, actress. Accidental drowning. Cocaine + Benadryl, Flexeril, Xanax.
- Michael Jackson (1958-2009). Singer. Homicide. MD administration of propofol, lorazepam, diazepam, & midazolam.
- Heath Ledger (1979-2008). Actor. Accidental. "died of the combined effects of five (5) prescription & one (1) over-the-counter medications: oxycodone, hydrocodone, diazepam, temazepam, alprazolam, and doxylamine (Unisom®)
- Mac Miller (1992-2018). Rapper, songwriter. Accidental overdose of fentanyl, cocaine & alcohol
- Prince Rogers Nelson (1958-2016) Accidental overdose of fentanyl
- Lil Peep (Gustav Ahr; 1996-2017). Rapper and singer. Multiple Xanax (alprozalam) pills. Blood showed traces of cannabis, cocaine, tramadol, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone, & oxymorphon.
Surging Rates of Opioid Deaths in the United States
Patterns among Adolescents 14-18 years old
I. Drug Mechanisms
Types of Drug Effects
- Antagonist: blocks
- Agonist: increases or mimics
- Mixed agonist-antagonists
Other Qualities of Drugs
- Affinity: tendency of a drug to bind to a receptor (strong to weak)
- Efficacy: tendency of a drug to activate a receptor (high to low)
A. Olds & Milner (1954): Dopamine & the Nucleus Accumbens
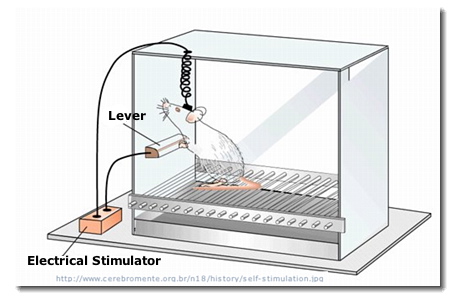
 James Olds & Peter Milner (1954)
found areas in rat's brain which leads to continual self-stimulation:
reinforcement via the nucleus accumbens.
James Olds & Peter Milner (1954)
found areas in rat's brain which leads to continual self-stimulation:
reinforcement via the nucleus accumbens.Dopamine carries more information than simple reinforcement, e.g., helping remember pleasure
Prediction Error Theory: The amount of dopamine released in the brain is a function of whether the value of a reward is greater than, equal to, or less than expected. When we are surprised by an experience (a great party, the ingestion of a new drug, etc.), more dopamine is released.
Tolerance and Withdrawal.Kent Berridge (U. Michigan) argues that there are two aspects of reinforcement that are different:
- Liking (giving pleasure) and
- Wanting, Desiring (motivation, grabbing attention, "salience")
His "Incentive Salience/Sensitivity Theory" proposes that
- Dopamine is not associated directly with pleasure, but
- Dopamine IS centrally involved in making an individual desire or want something intensely.
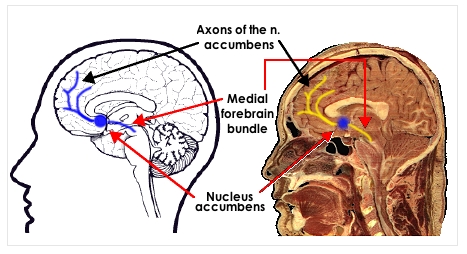
"Liking" or "pleasure" arises from a variety of "hot spots" in the brain (the yellow areas in the diagram on the right).
Attention-getting, Craving, Wanting, or Salience arises from the function of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and other sections of the mesolimbic system of the brain. Why? The brain has been "sensitized" (= has learned deeply) to all of the cues associated with a drug.
Individuals with addiction will have a powerful urge to get a drug even if there is no pleasure.
Some Drugs of Abuse (not in
book)
1. Stimulant drugs
(e.g., amphetamines, cocaine, etc.)
a. Amphetamine increases dopamine (DA) release from presynaptic terminals and also reverses the direction of the dopamine transporter (reuptake gate) which makes more DA available.
b. Cocaine ("coke") blocks the reuptake of DA, NE, and serotonin at the synapse.
c. Methylphenidate (Ritalin®): Stimulant currently prescribed for Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)
--> the use of Ritalin® when used as prescribed does not lead to the use of other drugs in later life.
e. MDMA (methylenedioxymethamphetamine or "Ecstasy")
![[Don't Smoke]](../graphics/no.smoking.jpg) 2. Nicotine
2. Nicotine![[Poppy Cultivation & Heroin]](../graphics/heroin.jpg)
Common opiates include
Opioid Receptors (= inhibitory G protein-coupled receptors)
- Opioid family of receptors. There are multiple places within the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system (as well as the digestive track) that are populated by opioid receptors. However, different types of opioid receptors are activated by different types of opioid molecules. There are four general classes of opioid receptors including the μ (mu) receptors which have a high affinity for morphine-like molecules [the other types are δ (delta), κ (kappa), and NOP (noiceptin/orphanin) receptors/]. Each of these types of receptors have a number of subtypes.
- Opioid receptors can be found on both the presynaptic terminal button and the postsynaptic membrane (see figure). Thus they are able to affect both the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron and the effects of neurotransmitters on the postsynaptic neuron.
- Opioid receptors within the central nervous system cause hyperpolarization in GABA neurons. Many of these GABA neurons normally restrain or inhibit the release of dopamine neurons. As a result, opiate receptors overall have the net effect of increasing the release of dopamine in the brain.
- Opiates decrease (inhibit) other opiate receptors & cause a range of effects such as analgesia (pain relief), decreased respiration, lowered motility of the GI system (anti-diarrhea), and physical dependence
A. Alcoholism or alcohol dependence
B. Alcohol (ethanol, ETOH): Inhibits Na+ ion flow across the neuron membrane; decreases serotonin activity, facilitates transmission at the GABAA receptor, blocks glutamate receptors, and increases dopamine activity. Thus, alcohol is mostly an INHIBITORY substance.
C. Types
a. Type I Alcoholism
b. Type II Alcoholism
D. Predispositions for Alcoholism & Substance Abuse
i. Alcoholism: Tends to be more likely among those who, as children, were described as impulsive, risk-taking, easily bored, sensation-seeking, & outgoing.
Associated with genes causing
- "long form" dopamine type 4 receptors: these receptors tend to be less sensitive to ETOH and, thus, people tend to consume more, and
- more active form of COMT (enzyme breading down DA) leading to lower levels of reinforcement & higher levels of impulsiveness.
ii. Among sons of alcoholics, alcoholism is associated with
- less than average intoxication after drinking a moderate amount of alcohol.
- experiencing more than average relief from tension after drinking alcohol.
- having a smaller than normal amygdala in the right hemisphere
iii. Genetic influences on drug abuse
- Strong evidence for polygenetic influences on alcoholism, cocaine use, and some other drugs.
iv. Environmental Influences
- Mothers who drink alcohol during pregnancy have children with a greater risk of alcoholism in later life
- Children with a variant gene for a less sensitive GABA receptor tend to have impulse control problems (including drug use) unless they grow up in families which clear parental supervision.
- Medications to Combat Opioid Abuse
- The most effective medical treatment for opioid (heroin, etc.) abuse in patients who have failed to "kick their habit" by more traditional treatment methods is the use of suboxone or methadone.
- Suboxone
- Methadone
- Note that our textbook says, "these drugs do not end the addiction. They merely satisfy the craving in a less dangerous way" (p. 472). When the alternative to suboxone and methadone is so frequently death, it would seem that keeping people alive ought to be the principal goal of health care providers.