|
|
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 03: Genetics and the Evolution of Behavior (OUTLINE) |
|
|
|
PSY 340 Brain and Behavior Class 03: Genetics and the Evolution of Behavior (OUTLINE) |
|
QUESTION: When we use the word "gene" what do we are we saying? What is a "gene"?
ANSWER: Two different (though related) meanings
(1) An inherited biological unit or factor that determines some physical trait [= Mendelian genetics]
and
(2) Inherited molecule(s) or sequences of DNA which give the code(s) or instructions for the production of specific proteins within cells [= Molecular genetics]
Examples of Mendian Traits
Dominant Trait
Recessive Trait
Tongue Rolling
Can Cannot Ear Lobe
Hangs free
Attached Hand Clasping
Left thumb on top
Right thumb on top Hitchhiker's thumb
Straight thumb
Bent thumb Hair Curly
Straight Other traits
Dimples No Dimples
Freckles No Freckles
Farsightedness Normal Vision
Normal Vision Nearsightedness
Low sensitivity to Poison Ivy High sensitivity to Poison Ivy
![[Gregor Mendel]](../photos/mendel.jpg)

Mendelian Genetics
• Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
• the rules of inheritance through genes
Molecular Genetics (DNA)
• chromosomes
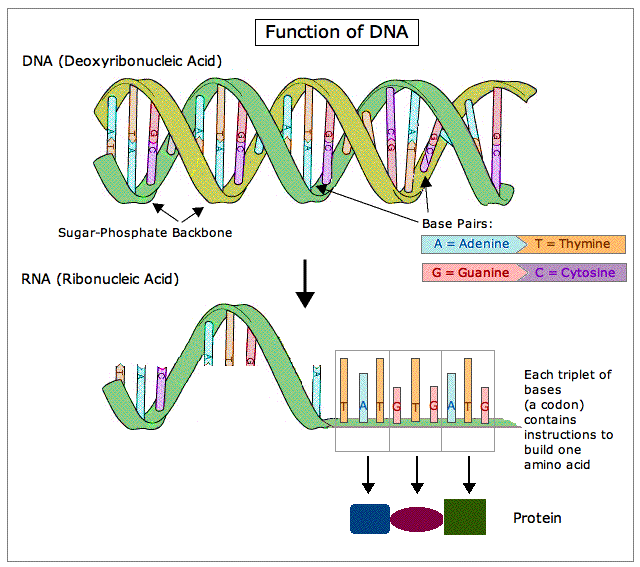
• DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid).
• James Watson and Francis Crick (discovered the shape)
• DNA → ribonucleic acid (RNA)(synthesize) → protein molecules (see figure "Function of DNA below).
![[Human Chromosomes]](../graphics/chromosomes_human.png)
Chromosomes & Genes
Human beings have 23 pairs of
chromosomes (see above)
Heritable (Simple) Traits [Mendelian Genetics]
![[Trait Transmission: Eye Color]](../graphics/trait_transmission.gif)
- dominant gene (D)
- recessive gene (r)
- homozygous (DD) or (rr): we or our parents have the same genes
- heterozygous for the trait (Dr) or (rD): we or our parents have differing genes
- dominant (D) ≠ most frequent
- Examples of significant physical disorders based upon Mendelian genetics (Dominant or Recessive genes)
- Albinism (recessive; the complete or partial absence of pigment in the skin, hair and eyes)
- Color blindness
- Cystic fibrosis
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Hemophilia
- Huntington's disease
- Phenylketonuria (will be discussed below)
- Sickle-cell disease
- Intermediate Traits: many traits which we once thought were
controlled by a single dominant vs. recessive gene are now known to be the results of multiple genes, e.g., at least 10 genes are involved in eye color.
Researchers on eye color found these additional genes when they looked not at simple color (brown vs. blue vs. hazel), but at very fine differences in the hue (actual color) and saturation (purity of the color) of thousands of eyes. They then compared these differences with the complete genomes of the individuals.
Genetic Changes (Molecular Genetics)
- Mutations: changes in base pairs (Adenine-Thymine; Guanine-Cytosine)
- E.g., Human FOXP2 gene vs. other primates...2 base pair differences( lead to language
- (Micro-)duplication or (micro-)deletion
Epigenetics: gene expression changes without modification of the DNA itself.
- Histone molecules
- Acetyl groups [COCH3] or methyl groups [CH3]
- Methyl group (CH3) inactivation
- transgenerational?
- diethylstilbestrol (DES): Mothers → "DES" Daughters → "DES" Granddaughters
Heredity & Environment
• many genes (= polygenetic inheritance) X environmental conditions
Heritability or the Heritability Index (H2): estimate of how much variation or differences in a characteristic across a population are due to differences in heredity. In a different sense, the heritabilty index tells us how much we can reduce our error of predicting whether one identical twin has a trait if the other twin has the trait.
- Range: 0 to 1
- Variability of the characteristic, NOT a measure of the average level of the characteristic.
Population Average BP 50% fall within the range of Heritability (H2) African American
145/87 127/77 to 150/93 0.70 Italian Americans 137/81 120/73 to 148/89 0.40
- we don't know why the AVERAGE BP is different between these groups and cannot say that genetics is the reason for the higher level among African Americans compared to Italian Americans
Research on heritability comes from
- Twin studies (looking at monozygotic (MZ) or identical twins [= from one egg] vs. dizygotic (DZ) or fraternal twins [= from two eggs])
- Recent research finds that "identical" twins actually develop some genetic mutation differences very early after conception and are not quite as identical as we had previously thought.
- Adopted children
- Examining specific genes
- Genome-wide Association Studies (GWAS) & Genome-wide Complex Trait Analysis (GCTA)
Problems in Heritability Research
- Some major findings about heritability
- "All psychological traits show significant and substantial genetic influence"
- "No (psychological) traits are 100% heritable" (usually 30%-50%)
- "Heritability is caused by many genes of small effect" (polygenetic inheritance)
- "Most environmental effects are not shared by children growing up in the same family" and genetic variability is usually more influential than environment in shaping differences among children.
- Difficult to tease apart genetic influences (heredity) from prenatal influences
- Multiplier Effect
Environmental Modification
The Evolution of Behavior
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Corrections to WRONG IDEAS about evolution
Brain Evolution: importance of cooking & change in gene for glucose transport to brain
An Evolving Understanding of Evolution
Evolutionary Psychology (aka SOCIOBIOLOGY) founded by Dr. Edward O. Wilson (Harvard U. Biologist died Dec. 26, 2021)
What are the evolutionary bases of behaviors? E.g., goose bumps, infant grasp reflex
Altruistic Behavior
• Simple altruism
• Reciprocal altruism: help others who will also help you (especially with cultural sanctions against "cheaters")
• Kin selection: help given to those who share same genetic inheritance
• Group selection (a controversial theory): cooperative groups do better than non-cooperative groups
- The material above reflects the "Modern Synthesis of Evolution" of the 1930s and 1940s which combined Mendel's ideas of heredity with Charles Darwin's Theory of Evolution. The discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule by Watson & Crick in 1953 seemed to have solidified the modern synthesis as a complete theory of evolution
- However, work in the last 20 years or so has argued that the modern synthesis has to be extended and modified. A variety of ways of extending the modern synthesis include
- Niche Construction Theory where organisms change the environment in which they live and, thus, affect future evolutionary paths
- Organism Development Theory which proposes that the way organisms grow and develop are major factors in how that organism can cope with its environment
- Multiple Inheritance Systems Theory: Beyond genes, there are three other systems of inheritance that affect organisms: epigenetics, behavioral patterns, and symbolic communication (language and similar systems).
- If this were a course in evolutionary biology, we would probably have to delve into these proposals to extend the evolutionary theory. But, we won't go beyond what is noted here.