Nov. 8, 2025 |
PSY 101
|
|
Nov. 8, 2025 |
PSY 101
|
|
Interpersonal Attraction: Liking & Loving
Interpersonal Attraction = Positive feelings toward another person
Key Factors in Attraction
1. Physical Attractiveness
- Matching hypothesis
2. Similarity
- Do opposites attract? Not really
3. Reciprocity
4. Other Factors
- Proximity and physical closeness
- Communication style
- Behavioral displays: standing/sitting closer, talking, eye gaze, smiling, mimicry
Perspectives on the Mystery of Love
Elaine Hatfield
(U Hawaii)
Ellen Berscheid
(U Minnesota)
Types: Passionate & Companionate
- Passionate Love
- Companionate Love
Love and Attachment
Cindy Hazan
(Cornell)
Phil Shaver
(UC Davis)Adult Attachment Styles
Youtube Video (4'19")
- Secure
- Avoidant
- Anxious (-Ambivalent)
Culture and Close Relationships
- the emphasis on passionate love in individualist Western culture is not universally found
- arranged marriages in collectivist cultures are generally as successful as romance-based marriages
Internet and Close Relationships
- Over the last 25 years, the growth of online relationship sites has massively expanded
- Online dating is the most common way US couples meet (52% of never-married Americans have tried online dating)
- About 1/3 of marriages in the US involve couples who met via the Internet
- Facebook: need to belong and to present ourselves positively ("impression management")
- Online Dating/Matching Sites use "matching algorithms" to pair couples
- Positive experiences tend to be reported for online dating sites. Maybe the algorithms work? Maybe there is a placebo effect?
- Some reports of negative outcomes: lying, financial exploitation, unwanted sexual aggression online
- Couples meeting online rather than in person may experience a somewhat lower level of relationship satisfaction overall & lower intensity of experienced love.
Attraction from an Evolutionary Perspective
- Facial Symmetry

- Waist-to-Hip Ratio of 0.70
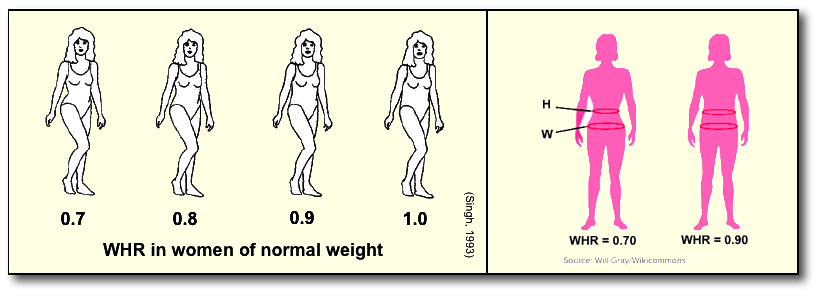
- Men: youthfulness & physical beauty in female
- Women: ambition, social status, financial potential in male
Attitudes: Making Social Judgments
Attitudes = positive or negative evaluations of objects of thought
- People (Trump, , Biden, Angelina Jolie), institutions (Le Moyne, the Catholic Church, the US Congress), groups (women, conservatives, Boy Scouts), political and social issues (gun control, tax cuts, health care reform, wearing masks).
Components & Dimensions of Attitudes
1. Cognitive: Beliefs
2. Affective: Feelings & emotions
3. Behavioral: Predisposition to act
Positive Attitude (Pro)
Negative Attitude (Anti)
Cognitive
Affective
Behavioral
Changing Attitudes: Factors in Persuasion
Source Message Channel Receiver
- High Credibility
- Expertise
- Trustworthiness
- Likability
- Attractiveness
- Similarity to ourselves
- Logical vs. Emotional
- Balance (1 vs. 2 sided): 2-sided often better
- Repetition = "mere exposure effect"
- Fear does work
- TV or Radio
- Personal
- Computer (Internet!)
- Personality
- Expectations
- Knowledge
- Strength of Pre-existing Attitude
Theories of Attitude Formation & Change
1. Learning Theory
- Classical Conditioning
- Operant Conditioning
- Observational Learning
2. Dissonance Theory (Leon Festinger)
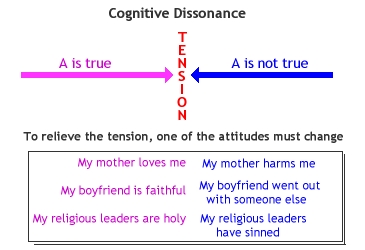
- Cognitive Dissonance: Two beliefs which directly contradict each other
- Effort Justification: We tend to change our attitude in a positive direction if we have put a lot of work into the object of the attitude
3. Elaboration Likelihood Model (Richard Petty & John Cacioppo)
- Central Route
- Peripheral Route
This page was originally posted on 11/07/03