Nov 4, 2025
Nov 4, 2025 |
PSY 101
|
|
Social Psychology: How an individual's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by others.
| Person
Perception: Forming Impressions of Others |

What factors go into the way we perceive or judge people?
A. Effects of Attractive Physical Appearance
- More handsome or beautiful people are thought to possess desirable personality characteristics
- Competence & intelligence
- Facial appearance
B. Stereotypes
= widely-held beliefs (within a specific culture) that people of a certain group have certain characteristics
≠ bias or discrimination (= acting on those beliefs)
C. Subjectivity in Person Perception
- Confirmation bias
- Illusory Correlations
D. Evolutionary Perspective
- "In Group" versus "Out Group" members

Attribution Processes: Explaining Behavior (to ourselves)
Attributions
= Inferences (conclusions or beliefs) people draw about the cause of events and their own and others' behaviors
A. Internal vs. External
Attributions
- Internal = due to traits and personal qualities
- External = due to situational factors or environmental constraints
B. Success or Failure Attributions: Stable vs. Unstable Causes
Bernard Weiner's
2-Dimension Theory
Dimension 2 (Stability) Unstable
(Temporary)Stable
(Permanent)Dimension 1
(Self or Not)
Internal Mood, Feeling
"I've been worried about some stuff at home and it interfered with my last job rating."
Ability, IQ
"They realized that I don't have the skills necessary for the job"
External Luck, Chance
"The company had to lay off employees because the economy is in a dip these days"
Changes in the World
"The jobs have moved overseas and the company can't afford American workers any more."
 C.
Biases in Attributions
C.
Biases in Attributions
1. Actor-Observer Bias
Actor = the one doing something (acting)
Observer = the one watching someone else (observing)
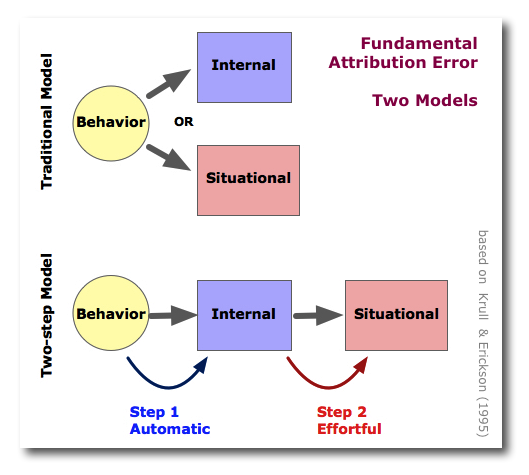
->>>> Fundamental Attribution Error !!!!!!!!!!!!
- We tend to attribute our own behaviors to situations (external)
- We tend to attribute others' behaviors to personal qualities (internal)
(probably the most important theory in social psychology)
In general, actors favor external attributions while observers favor internal attributions
2. Self-Serving Bias (giving yourself the benefit of the doubt)
D. Culture & Attributions
Cultures defined by Harry Triandis (above, left) as
Individualist
- versus Japan's "self-effacing" bias
Collectivist
Geert Hofstede
What are the ties like between individuals?
- "Loosely bonded" cultures (Individualist)
vs.
- "Tightly bonded" cultures (Collectivist)
This page was originally posted on 11/05/03