Brain
- 3 pounds
- about 86 billion (+/- 8 billion) neurons
& about 84 billion glial cells
|
| B. Hindbrain |
|
|
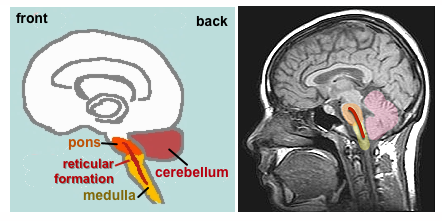 |
Cerebellum |
Large, folded
structure behind the brainstem.
- Coordination
of movement & balance
- Smooth
motion
- Fine
(intricate) motor skills
- Conditioned
learning
- NEW: role
in cognition (thinking), language, & affect
(emotion)
|
brainstem = medulla
& pons (below)
|
| Medulla |
- Regulation
of fundamental bodily activities such as breathing
and blood circulation. Major damage to the medulla
often results in death.
- Muscle
tone
- Reticular Formation: runs in middle of medulla, pons,
& into midbrain. Modulates breathing, pain,
& centrally involved in sleep, awakening &
arousal.
|
|
Pons
("The Bridge")
|
- Pathway
between the Cerebellum
and the Cerebrum (see
below)
- Connects
the Cerebrum above with the brain stem & the
spinal cord below. A pathway for motor instructions
to the spinal cord and for sensory information from
the spinal cord to the thalamus (see below)
|
|
C.
Midbrain
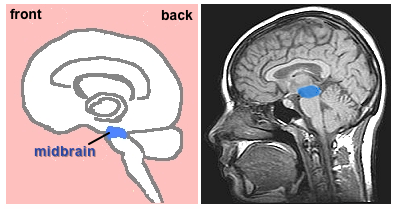 |
Segment of
top of the brainstem lying between the pons and the
forebrain.
- Sensitive
to orientation of individual in space; works with
voluntary muscle movement, e.g., moving head to
respond to someone's call or a strange sound in the
environment; tracking an object like a baseball to
catch it
- Dopamine-releasing
neurons project from the midbrain into the
forebrain. The gradual death of these neurons is
associated with the development of Parkinson's
Disease.
|
| D.
Forebrain |
|
|
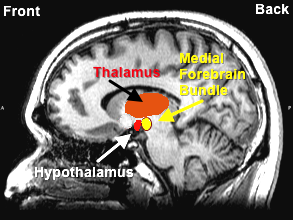
| i. Thalamus |
- Relay
station for all incoming sensory information
(vision, hearing, touch, etc.) except for smell.
Information is passed on to cerebrum.
- Beginning
of the integration of this information.
|
ii. Hypothalamus
|
- Regulation
of basic bodily needs & functions; maintains
body's biological homeostasis (balance), e.g.,
temperature, heart rate, blood pressure
- Control of
the autonomic nervous system: fighting vs.
relaxation.
- Basic
biological drives: feeding, thirst, sex
- Sends
various signals to the pituitary gland to release
hormones
|
|
iii. Limbic System
![[Limbic
System]](../psy101graphics/limbic.jpg)
|
- A loose
network of structures which, together, appear to be
involved in the regulation and expression of
emotion and pleasure. These structures include
the hippocampus, septum, amygdala, parts of the
thalamus & hypothalamus, and several other
structures.
- Since they
lie on the border between the cerebral cortex and
lower/deeper structures, they were labeled as the
"limbic" system by Paul MacLean in 1954 (limbus in Latin
= border or edge).
|
|
Hippocampus
- Human
memory processes. Long-term storage (consolidation)
of memories. We learned this from Patient H.M.
Amygala
- Using many
inputs from the sensory system, it evaluates the
environment vis-a-vis emotion.
- Particularly
involved in weighing threats in the environment and,
thus, signalling whether we might need to be anxious
or fearful (researched by Joseph LeDoux at NYU)
Medial Forebrain Bundle
(part of limbic system & passing through the
hypothalamus)
- Olds &
Milner (1954) discovery of self-stimulation centers
in rats' brains = "pleasure centers"
- DA-rich
neurons which, when stimulated, result in
pleasure/reward as well as a sense of salience
(wanting/desiring)
|
| iv. Cerebrum |
The
largest and most complex part of the human brain. |
![[Cortex Top View]](../psy101graphics/redcortexsuperior.jpg)
![[Cortex Bottom View]](../psy101graphics/redcortexinferior.jpg) |
Cerebral
Cortex = The outer layer of the cerebrum.
Deeply folded and compacted
Cerebral Hemispheres. The cerebrum is
divided into two hemispheres. The right and left
hemispheres are separated by a deep longitudinal
fissure. Deep below the outer cortex, the two
hemispheres are connected by a thick bundle of fibers
called the corpus callosum.
![[Cerebrum]](../psy101graphics/cerebrum.png)
|
|
Lobes of the Brain
![[Lobes of the
Brain]](../psy101graphics/lobes.jpg)
|
Frontal Lobe |
- Primary
motor cortex: initiation of movement (lighter blue
in diagram)
- Prefrontal
cortex: area in front of motor cortex (deep red in
diagram)
- Executive
functions: Goal planning, making decisions,
considering context
|
| Parietal Lobe |
- Primary
processing area for sense of touch and the other
somatosensory senses (temperature, pressure,
proprioception, etc.; darker blue in diagram)
- Processes
the spatial aspects of behavior (e.g., where the
body is located in space; lighter blue in diagram).
|
| Temporal Lobe |
- Primary
auditory processing area
- Comprehension
of spoken language
- Processes
visual data to recognize faces, objects, and what
they are called
|
| Occipital Lobe |
- Primary
visual processing area
|
 B. The Central
Nervous System (CNS)
B. The Central
Nervous System (CNS)
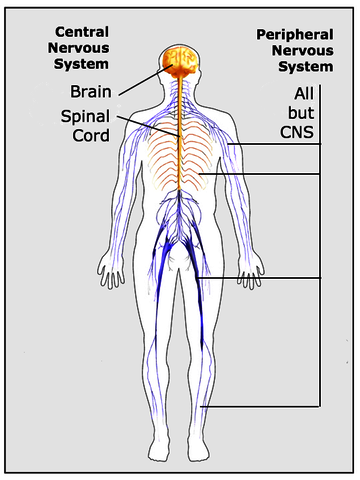 1. Organization of
the Nervous System
1. Organization of
the Nervous System![[Cat
Scan Hemorrhage]](../psy101graphics/catscan1319_04.jpg)
![[Cat
Scan Tumor]](../psy101graphics/catscan1319_19.jpg)
![[MRI
Image Tumor]](../psy101graphics/mriscan1319_25.jpg)
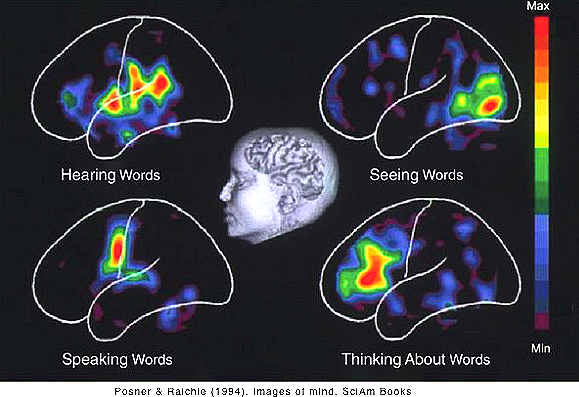
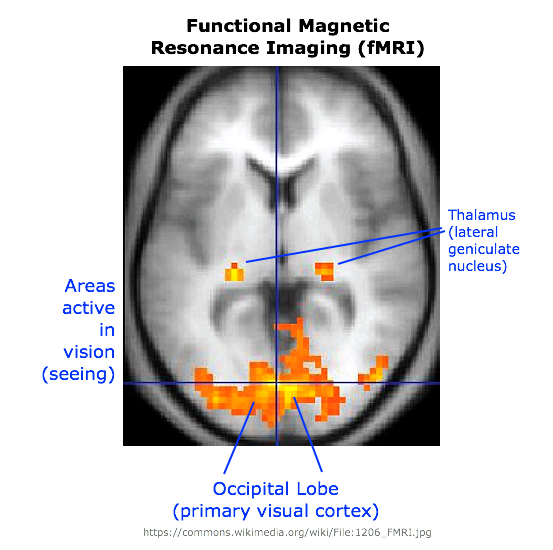
 PET (Positron Emission
Tomography)
PET (Positron Emission
Tomography)![[Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation]](../psy101graphics/tms.jpg)


![[Limbic
System]](../psy101graphics/limbic.jpg)

![[Cortex Top View]](../psy101graphics/redcortexsuperior.jpg)
![[Cortex Bottom View]](../psy101graphics/redcortexinferior.jpg)
![[Cerebrum]](../psy101graphics/cerebrum.png)
![[Lobes of the
Brain]](../psy101graphics/lobes.jpg)
![[Paul Broca]](../psy101graphics/broca.jpg)
![[Tan's Brain]](../psy101graphics/tan.jpg)
![[Broca &
Wernicke's Areas]](../psy101graphics/aphasias.jpg)
![[Paul
Wernicke]](../psy101graphics/wernicke.jpg) Wernicke
Wernicke![[Roger
Sperry]](../psy101graphics/sperry.jpg)
![[Split
Brain Research Model]](../psy101graphics/splitbrain.jpg) Roger
Sperry, Michael Gazzaniga, and their associates
studied the functional psychological effects of "
Roger
Sperry, Michael Gazzaniga, and their associates
studied the functional psychological effects of "