Updated September 11, 2025
| PSY
101
Updated September 11, 2025
|
||


What if you became like Jason Bourne (Matt Damon's character) in the 2002 movie?
What would it be like to wake up some morning here at Le Moyne (or at home) with the kind of memory loss of Jason Bourne, that is, you can DO various things, but you haven't the slightest clue who or where you are? What would that be like? What would you do?
If any one of these kinds of memory no longer works right, you will be a very different kind of person
Three Processes or Activities involved in Memory
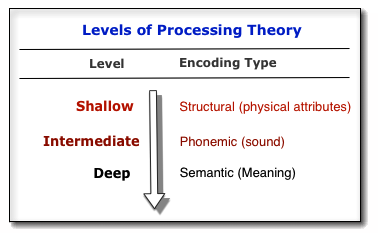 Levels of
Processing Theory (see diagram on right)
Levels of
Processing Theory (see diagram on right)Craik & Tulving (1975) Experiments
- Students shown a list of 60 words on a screen with each word presented for 6 seconds
- Each student was asked to pay attention to one of three questions about each word
- One category of questions (shallow) were about how the word were presented visually (Word: "Is the word shown in CAPITAL LETTERS?").
- The second category of questions (intermediate) were about the phonemic qualities of the word ("Does the word rhyme with the word "bee"?).
- The third category of questions (deep) were presented so that the reader was forced to think about what the word means or what category the word falls in [semantic] ("Can you meet one in the street [a friend]"?)
Example words and questions used
Word
Format
"is the word capitalized?"
Rhyme
"does it rhyme with...?"
Question
"Is it...?"
Speaking
SPEAKING
leaking
a way to communicate
Gun
gun
fun
a type of weapon
Grass
GRASS
class
a type of plant
Witch
witch
pitch
something associated with magic
- After seeing the words, they were given a list of 180 words (60 they had seen and 120 they had not seen). They were asked if they had seen them or not (Yes or No). How well they recalled the words was directly related to the level they first processed each word:
- Implication for studying in college?
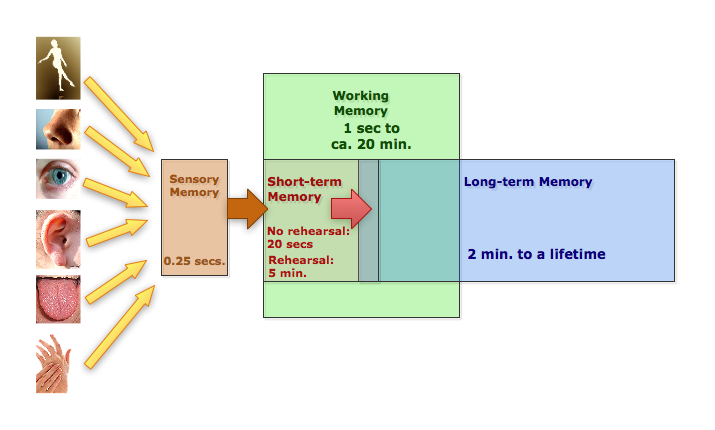
![[Atkinson & Shifrin Model]](../psy101graphics/atkinson_shifrin_model.jpg)
A. Sensory Memory = Information is maintained in its sensory form (visual, auditory, etc.) for a very brief period of time (ca. 0.25 secs.)
B. Short-term Memory (STM) = a limited capacity story that can maintain unrehearsed information for up to about 20 seconds
- Rehearsal
- Capacity of Storage
- George A Miller's "Magic Number 7 +/- 2" (1956)
- More recent work suggests that the capacity of STM is probably smaller than Miller suggested (4 plus/minus 1).
- Chunking of information: grouping familiar or similar stimuli as a single unit
- Could you memorize this string of numbers easily? 177618121861189819171941
- 1776 • 1812 • 1861 • 1898 • 1917 • 1941
![[Baddeley's Working Memory]](../psy101graphics/baddeley_workingmemory.jpg) Allan
Baddeley's "Working Memory" (2001) Model (see diagram)
Allan
Baddeley's "Working Memory" (2001) Model (see diagram)Working memory = a modular system for the temporary storage and manipulation of information
Four components
- Phonological rehearsal loop
- Visuo-spatial sketch pad
- Episodic buffer (temporarily pulling in information from Long Term Memory)
- Executive Control System
Working memory capacity (WMC) = the ability to hold & manipulate information in conscious attention
- Stable personal trait
- Can be reduced by situational factors like stress or worry.
LTM = an unlimited capacity store that can hold information over lengthy periods of time

- Flashbulb Memories (see image above) = when experiencing dramatic and important events, people report unusually vivid and detailed recollections.
- For example, e.g., Kennedy Assassination in 1963; Human landing on moon in 1969; Death of Princess Diana in 1997; the 9/11 attacks in 2001, the election of Barack Obama (2008) & Donald Trump (2012), the deaths of Kobe Bryant or George Floyd (2020)
- Research has shown that these memories are neither as accurate nor complete as people either think or early theorists believed.
- Vividness ≠ accuracy
1. Using Cues to Aid Retrieval
2. Reinstating the Context of an Event
- Tip of the Tongue phenomenon
- Retrieval cues
3. Relying on Schemas
Schema = an organized cluster of knowledge about a particular event or object abstracted from previous individual instances or experiences.
- What are the schemas for college professor? high school jock? lawyer? clergy? Army soldier?
Consider what you might think an NFL professional football player looks like. Suppose you saw a 10-second video clip of a player being interviewed in a locker room. What would you tend to remember?
- We tend to remember facts consistent rather than inconsistent with our schemas
- You might remember that he was wearing his uniform or carrying his helmet, but would probably not remember that he was holding a copy of a newspaper in his hand.
- HOWEVER, we tend to remember facts that are clash significantly with our schemas
- If that football player was holding a bouquet of roses in his hand or putting on a fur coat, we'd probably remember that fact.
4. Reconstructing Memories
- KEY NOTION: Contemporary psychology shows that memories are NOT like a videotape machine playing back something that was previously recorded. Our brains are not stamped with exact copies of our experiences.
- Rather, recalled memories are reconstructions !!!!!!! of what we have experienced in the past at varying levels of accuracy. We rebuild again each time we remember something.
- Misinformation Effect = a participants recall of events is altered by misleading information introduced after the event
- First described by psychologists Elizabeth Loftus
- Eyewitness testimony is probably the weakest type of evidence.
YouTube Video explaining her work (begin at 1.48 until 6:50): from Psychology Unlocked (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-tbwrUYqytQ)
5. Source Monitoring
- Mistakes in memory retrieval are often due to source-monitoring errors
- For example, you may have read some story about a celebrity or a politician and failed to notice that the story came from a suspect source such as the National Enquirer or some other gossip publication.
- "Fake-News": Look over some of the suspect stories on a site like the Tampa Bay Times' Politifact.com ("Pants on Fire" Lie list). Particularly in the last 10 years, there have been all sorts of made-up or phony stories and, even, "deepfake" images & movies posted online. For example, using Photoshop a fake photo of Obama shaking hands with the President of Iran was circulated by various anti-Obama politicians. The actual photo from 2011 was Obama meeting the Prime Minister of India to discuss nuclear arms control. In the age of Artificial Intelligence, this is only getting more common.
Another excellent source to check if something online is true is Snopes.com (https://www.snopes.com) [NOT Snopes2.com]