|
PSY
101
Class 03 Development
I: Prenatal & Childhood Development (Outline)
|
||
| Johnny W. (Kristof, 2014, Feb. 22 & 2014, Mar. 02, NY Times) |
Alex R. |
 Johnny is a 3 year old, happy and friendly kid
born to a single White mother. He lives in Point
Pleasant, WV in a trailer with his mom who doesn't have
enough money to fix her broken car. Johnny is a 3 year old, happy and friendly kid
born to a single White mother. He lives in Point
Pleasant, WV in a trailer with his mom who doesn't have
enough money to fix her broken car.
|
Alex is a 3 year old, happy, and friendly kid
born to married White parents. He lives in Manlius, NY.
His father is an engineer and his mother teaches school in
the Fayettevile-Manlius (F-M) school system.
|
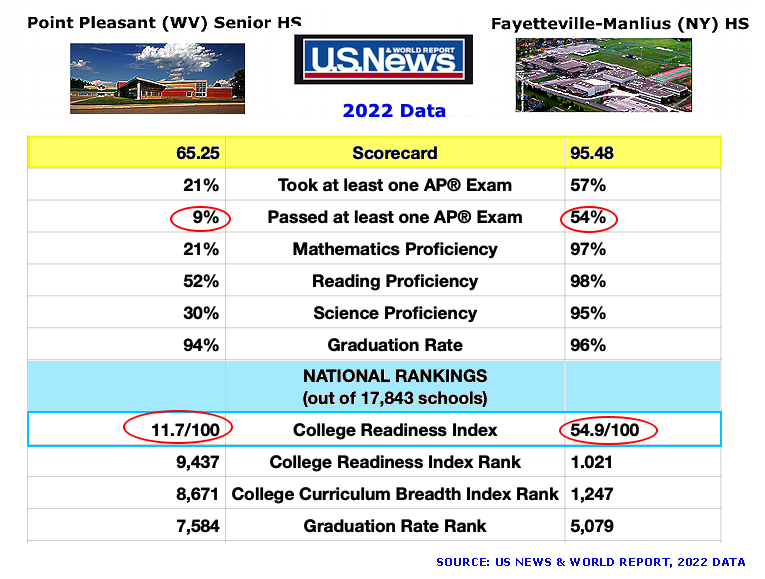
How do you think each of these children will develop over the next twenty years?
What are the most important factors affecting how these children will develop?
| Prenatal Development |
Stages
1. Germinal: Conception to 2 weeks
- Zygote
- Placenta
2. Embryonic State: 2 to 8 weeks
3. Fetal State: 8 weeks to 38 weeks
Environmental Risk Factors to Fetal Development
1. Maternal Malnutrition2. Stress & Emotion
3. Maternal Drug Usage
4. Maternal Alcohol Consumption

- Drinking may lead to Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) or other Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)
5. Maternal Illness (Infections)
- In recent years, research has found far higher levels of FAS/FASD than previously thought
- Old estimate: 0.5 to 2-3 per 1000 births for FAS and 10 per 1000 births for FASD
- New (conservative) estimate: 11 to 50 per 1000 births for FASD (= 1.1 to 5% of all US child births)
- Many (even most) cases are probably not diagnosed
- Even "moderate" levels of drinking can have negative effects on developing child
- No safe level of drinking in pregnant women
6. Environmental Toxins
7. Fetal Origins of Adult Diseases
| Early Childhood |
Physical & Motor Development: Exploring the world
Pattern = (1) cephalocaudal (head-to-foot) & (2) proximodistal (center-outwards)
Maturation = development which comes from the unfolding of genetic blueprint
Developmental Norms
- Typical form
- Variation in motor development
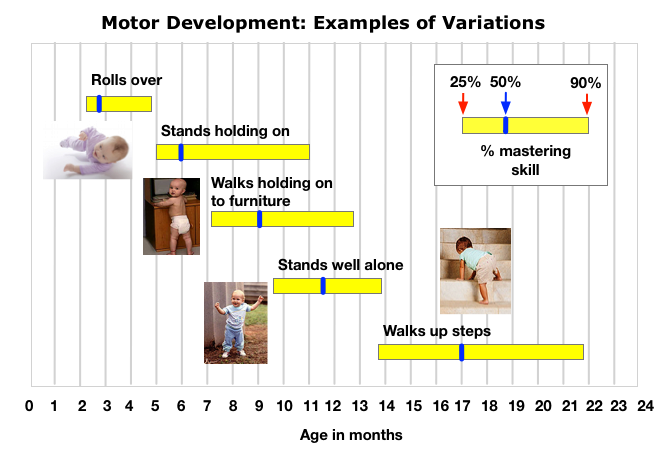
Cultural Variations
Temperament: Easy & Difficult Babies [Not in text, but important]
- Temperament = characteristic mood, activity level, & emotional reactivity
- Thomas & Chess: Longitudinal Study
- Easy (40%)
- Slow-to-Warm-Up (15%)
- Difficult (10%)
Early Emotional Development: Attachment
- Attachment = close, emotional bond of affection between child & caregivers
- Separation Anxiety = emotional distress shown by infant when separated from those whom they are attached to
- Patterns of Research by Harry Harlow & Mary Ainsworth


- Harlow's Baby Monkeys prefer cloth-covered to wire-covered "substitute mothers"
- The Strange Situation: Experimental study of children's attachment to parents
- Ainsworth devised an experimental situation in which children between the ages of 14 and 24 months of age could be observed.
- YouTube: 3'14"
1. Secure Attachment
2. Anxious-Ambivalent (Resistant)
3. Avoidant
4. Disorganized (not in book)
- Child develops an internal working model of the dynamics of close relationships
Cultural Differences in Attachment
Communicating: Language Development
Toward Words
Using Words
Parent-Infant Speech & Language Learning
- Talking to Children Matters => Early Language Experience Strengthens Processing and Builds Vocabulary
| Personality Development: Erikson's Theory |
1. Certain (invariant) order
2. Age-related
3. Qualitative change (discontinuous from past stages)
Erik Erikson (1902-1994)
We develop within a psychosocial world and face demands at each stage of development to grow and change.
Developmental Stage
(Approx. Age)
Freudian Stage
(Psychosexual)
Erikson's Stage
(Psychosocial)
Infant (0-1 yo)
Oral Basic Trust vs. Mistrust
Toddler (2-3)
Anal
Autonomy vs. Self-Doubt
Early Childhood (4-6)
Phallic Initiative vs. Guilt
Late Childhood (7-12) Latency Industry vs. Inferiority
Adolescence (13-18) Genital
Ego Identity vs. Role Confusion
Adult Transition (19-26)
(Not examined
by Freud)
Intimacy vs. Isolation
Early/Middle Adulthood (26-55)
Generativity vs. Self-Absorption
Later Adulthood/Old Age (55+)
Integrity vs. Despair
1. Trust versus mistrust (~ birth to about 2 years old)
2. Autonomy vs. Shame-Doubt (~ ages 2-3)
3. Initiative vs. Guilt (~ ages 4 to 6)
4. Industry vs. Inferiority (~ ages 7 through 12)
Here is a diagram of the most important stage theories in current psychology (pdf version)Evaluation of Erikson's Theory